Volume 31, Number 7—July 2025
Research Letter
Fatal Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure Caused by Burkholderia thailandensis, China
Figure
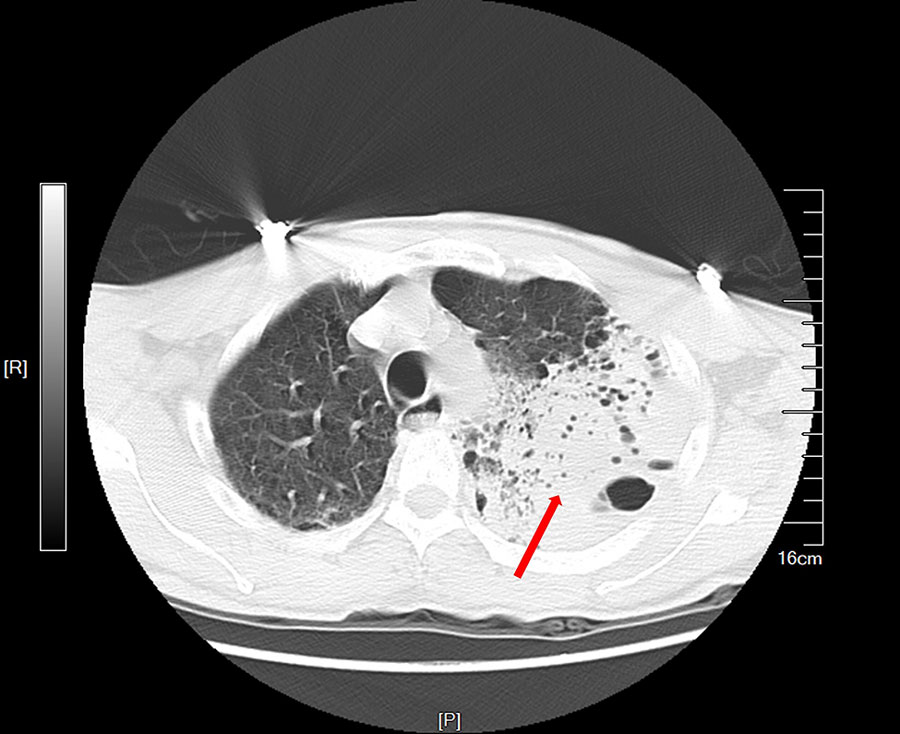
Figure. Chest computed tomography scan of patient who died of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure caused by Burkholderia thailandensis, China. Scan shows left lung consolidation and pleural effusion. Red arrow indicates a large high-density shadow in the left lung field. Scale indicates actual size of anatomical structures and lesions. P, posterior; R, right.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: April 23, 2025
Page updated: June 25, 2025
Page reviewed: June 25, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.