Volume 31, Number 8—August 2025
Research Letter
Seroprevalence of Rift Valley and Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses, Benin, 2022–2023
Figure 2
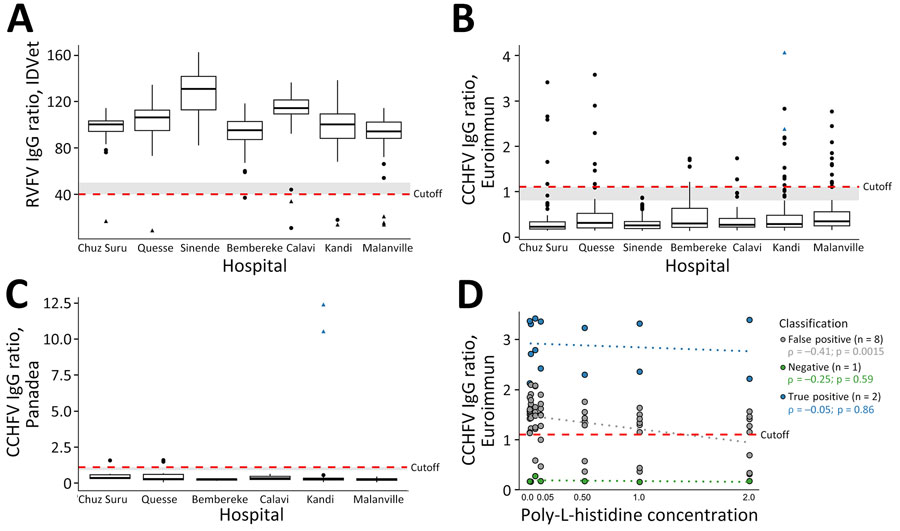
Figure 2. ELISA reactivity for Rift Valley and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever viruses, Benin, 2022–2023. IgG ELISA (ID.Vet, https://bioadvance.life/en/id-vet-2) for RVFV for which a sample/negative percentage <40.0 is considered positive. IgG ELISAs (Euroimmun, https://www.euroimmun.com; Panadea Diagnostics, https://www.panadea-diagnostics.com) for CCHFV for which ratios >1.1 are considered positive according to the manufacturer. A) RVFV competitive ELISA (ID.Vet) using nucleoprotein as antigen. Positive samples, n = 10/650. B) CCHFV indirect ELISA (Euroimmun) using nucleoprotein as antigen. Positive samples, n = 40/650. C) CCHFV immune complex capture ELISA (Panadea) using nucleoprotein as antigen. Positive samples, n = 5/92. D) Reduced indirect IgG ELISA reactivity of CCHFV (Euroimmun) with poly-L-histidine concentrations of 0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.50, 1.00, and 2.00 mg/mL. Box plots show sample distribution, displaying medians (thick lines within boxes) and interquartile ranges (box top and bottom edges); whiskers indicate 1.5× interquartile range. Red lines show cutoff levels for ELISAs; gray shading shows the area for borderline results; black triangles show samples positive by RVFV immunofluorescence assay; blue triangles show samples positive by CCHFV immunofluorescence assay. The Spearman correlation was performed in R, and boxplots for RVFV and CCHFV were plotted using the ggplot2 package in R (https://www.r-project.org). Because of the low detection rates of RVFV-specific and CCHFV-specific IgG, negative reverse transcription PCR results, and low serum volumes, we did not perform IgM analyses. CCHFV, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus; RVFV, Rift Valley fever virus.