Volume 31, Number 8—August 2025
Research Letter
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Acquired through Dog Bite, South Korea
Figure
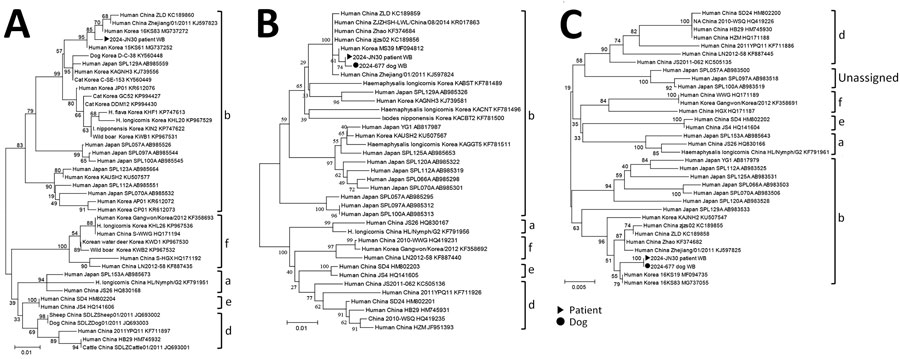
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of SFTSV small (321 bp) (A), medium (477 bp) (B), and large (696 bp) (C) segments from human patient and dog, South Korea. Clustal X version 2.1 (http://www.clustal.org/clustal2) was used to construct the phylogenetic trees by using neighbor-joining with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Genotypes of SFTSV are labeled (a, b, d, e, f). BLASTn (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) analysis revealed and nucleotide identity with reference SFTSV strain MF094812 of 99.44% (534/537) for the patient sample and 99.45% (541/544) for the dog sample; nucleotide identity with reference SFTSV strain MF094735 was 99.62% (785/788) for the patient sample and 99.63% (802/805) for the dog sample. The large segment nested PCR results showed 100% identity between the 2 samples. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site. SFTSV, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.