Volume 31, Number 9—September 2025
Research
Increased Incidence of Candida auris Colonization in Early COVID-19 Pandemic, Orange County, California, USA
Figure 2
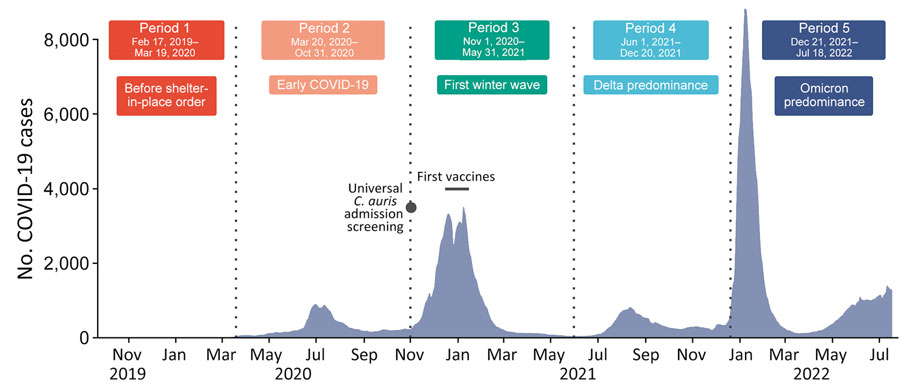
Figure 2. Seven-day moving averages of new daily COVID-19 cases in Orange County, California, USA, across 5 time periods during study of Candida auris colonization early in the COVID-19 pandemic. Black dot represents beginning of C. auris screening. Horizontal black bar represents period in which COVID vaccines first became available.
Page created: July 09, 2025
Page updated: August 26, 2025
Page reviewed: August 26, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.