Volume 31, Number 9—September 2025
Research
Insights into Infant Strongyloidiasis, Papua New Guinea
Figure 3
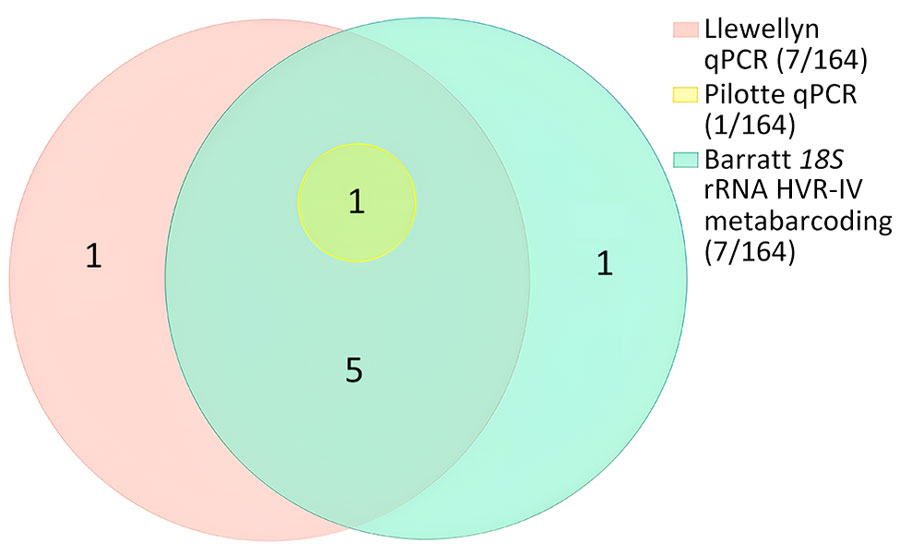
Figure 3. Euler diagram showing the performance of 2 qPCRs (20,21) and 18S rRNA HVR-IV metabarcoding (16) for the detection of Strongyloides spp. in 164 infant fecal samples from Papua New Guinea. Values in parentheses are no. positive samples/total no. tested. HVR, hypervariable region; qPCR, quantitative PCR.
References
- Bradbury RS. Strongyloides fuelleborni kellyi in New Guinea: neglected, ignored and unexplored. Microbiol Aust. 2021;42:169–72. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Page W, Shield J, O’Donahoo F, Miller A, Judd J, Speare R. Strongyloidiasis in Oceania. In: Hotez PT, editor. Neglected tropical diseases-Oceania. Switzerland: Springer; 2016. p. 69–99.
- Viney M, Ashford R, Barnish G. A taxonomic study of Strongyloides Grassi, 1879 (nematoda) with special reference to Strongyloides fuelleborni von Linstow, 1905 in man in Papua New Guinea and the description of a new subspecies. Syst Parasitol. 1991;18:95–109. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Kelly A, Voge M. Report of a nematode found in humans at Kiunga, Western District. P N G Med J. 1973;16:59.
- Muller R, Lillywhite J, Bending JJ, Catford JC. Human cysticercosis and intestinal parasitism amongst the Ekari people of Irian Jaya. J Trop Med Hyg. 1987;90:291–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ashford RW, Barnish G, Viney ME. Strongyloides fuelleborni kellyi: infection and disease in Papua New Guinea. Parasitol Today. 1992;8:314–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Viney ME, Ashford RW. The use of isoenzyme electrophoresis in the taxonomy of Strongyloides. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1990;84:35–47. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barnish G, Ashford RW. Strongyloides cf fuelleborni in Papua New Guinea: epidemiology in an isolated community, and results of an intervention study. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1989;83:499–506. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ashford RW, Vince JD, Gratten MJ, Bana-Koiri J. Strongyloides infection in a mid-mountain Papua New Guinea community: results of an epidemiological survey. 1979. P N G Med J. 2005;48:58–65.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vince JD, Ashford RW, Gratten MJ, Bana-Koiri J. Strongyloides species infestation in young infants of Papua New Guinea: association with generalized oedema. 1979. P N G Med J. 2005;48:50–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barnish G, Harari M. Possible effects of Strongyloides fuelleborni-like infections on children in the Karimui area of Simbu Province. P N G Med J. 1989;32:51–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- King SE, Mascie-Taylor CGS. Strongyloides fuelleborni kellyi and other intestinal helminths in children from Papua New Guinea: associations with nutritional status and socioeconomic factors. P N G Med J. 2004;47:181–91.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dorris M, Viney ME, Blaxter ML. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the genus Strongyloides and related nematodes. Int J Parasitol. 2002;32:1507–17. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hasegawa H, Hayashida S, Ikeda Y, Sato H. Hyper-variable regions in 18S rDNA of Strongyloides spp. as markers for species-specific diagnosis. Parasitol Res. 2009;104:869–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Aupalee K, Wijit A, Singphai K, Rödelsperger C, Zhou S, Saeung A, et al. Genomic studies on Strongyloides stercoralis in northern and western Thailand. Parasit Vectors. 2020;13:250. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barratt JLN, Lane M, Talundzic E, Richins T, Robertson G, Formenti F, et al. A global genotyping survey of Strongyloides stercoralis and Strongyloides fuelleborni using deep amplicon sequencing. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13:
e0007609 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Hino A, Tanaka T, Takaishi M, Fujii Y, Palomares-Rius JE, Hasegawa K, et al. Karyotype and reproduction mode of the rodent parasite Strongyloides venezuelensis. Parasitology. 2014;141:1736–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ko PP, Haraguchi M, Hara T, Hieu DD, Ito A, Tanaka R, et al. Population genetics study of Strongyloides fuelleborni and phylogenetic considerations on primate-infecting species of Strongyloides based on their mitochondrial genome sequences. Parasitol Int. 2023;92:
102663 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - de Ree V, Nath TC, Barua P, Harbecke D, Lee D, Rödelsperger C, et al. Genomic analysis of Strongyloides stercoralis and Strongyloides fuelleborni in Bangladesh. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024;18:
e0012440 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Llewellyn S, Inpankaew T, Nery SV, Gray DJ, Verweij JJ, Clements AC, et al. Application of a multiplex quantitative PCR to assess prevalence and intensity of intestinal parasite infections in a controlled clinical trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:
e0004380 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Pilotte N, Papaiakovou M, Grant JR, Bierwert LA, Llewellyn S, McCarthy JS, et al. Improved PCR-based detection of soil transmitted helminth infections using a next-generation sequencing approach to assay design. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:
e0004578 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Jiang H, Lei R, Ding S-W, Zhu S. Skewer: a fast and accurate adapter trimmer for next-generation sequencing paired-end reads. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15:182. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods. 2016;13:581–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Janwan P, Rodpai R, Intapan PM, Sanpool O, Tourtip S, Maleewong W, et al. Possible transmission of Strongyloides fuelleborni between working Southern pig-tailed macaques (Macaca nemestrina) and their owners in Southern Thailand: Molecular identification and diversity. Infect Genet Evol. 2020;85:
104516 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Pampiglione S, Ricciardi M. Geographic distribution of Strongyloides fulleborni in humans in tropical Africa. Parasitologia. 1972;14:329–38.
- Hira PR, Patel BG. Human strongyloidiasis due to the primate species Strongyloides fülleborni. Trop Geogr Med. 1980;32:23–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barratt JLN, Sapp SGH. Machine learning-based analyses support the existence of species complexes for Strongyloides fuelleborni and Strongyloides stercoralis. Parasitology. 2020;147:1184–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kelly A, Little MD, Voge M. Strongyloides fulleborni-like infections in man in Papua New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976;25:694–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barnish G, Ashford RW. Strongyloides cf. fuelleborni and hookworm in Papua New Guinea: patterns of infection within the community. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1989;83:684–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brown RC, Girardeau HF. Transmammary passage of Strongyloides sp. larvae in the human host. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977;26:215–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Constable P, Hinchcliff K, Done S, Grünberg W. Diseases of the alimentary tract: nonruminant. Veterinary medicine. 11th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier; 2017.
- Uzal FA, Plattner BL, Hostetter JM. Alimentary system. In: Maxie M, editor. Jubb, Kennedy & Palmer’s pathology of domestic animals. 6th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2016. p. 1–257.e2.
- Dey-Hazra A, Sallmann HP, Enigk K, Harisch G. Protein synthesis changes in the liver of piglets infected with Strongyloides ransomi. Vet Parasitol. 1979;5:339–51. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Verweij JJ, Canales M, Polman K, Ziem J, Brienen EA, Polderman AM, et al. Molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis in faecal samples using real-time PCR. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009;103:342–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: July 15, 2025
Page updated: August 26, 2025
Page reviewed: August 26, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.