Volume 32, Number 1—January 2026
Dispatch
Evidence of Rat Hepatitis E Virus Circulation through Wastewater Surveillance, Central Argentina
Figure 2
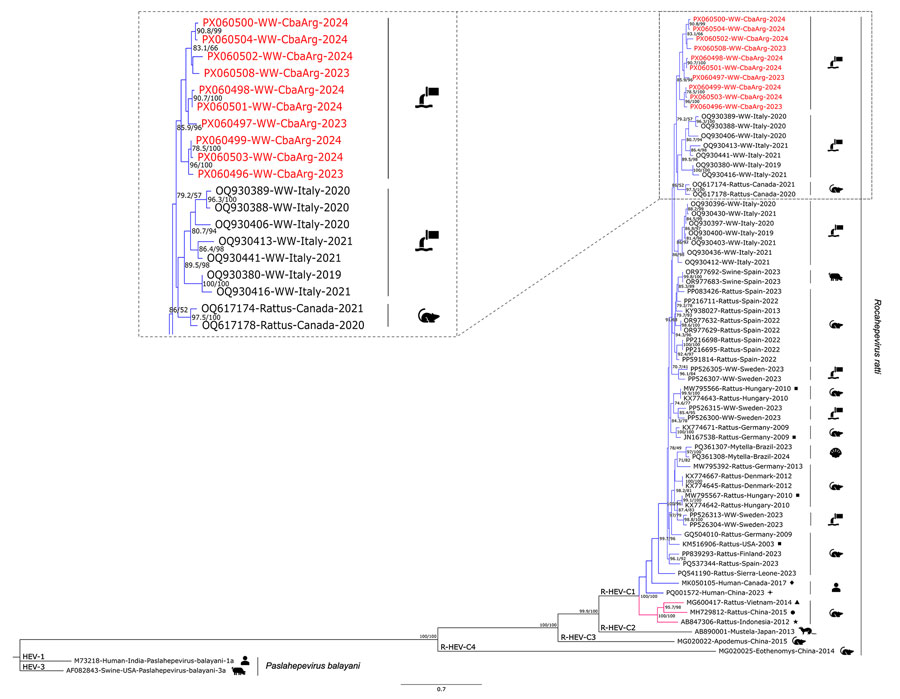
Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree on the basis of a 338 bp fragment of the open reading frame 1 genomic region of rat hepatitis E virus (R-HEV; Rocahepevirus ratti) from Argentina, 2023–2024. Red text indicates sequences obtained during this study. The tree includes representative sequences of each R-HEV genotype available in GenBank database, additional sequences of proposed clades (clade I in blue, clade II in pink) and subtypes a (square), b (circle), c (5-pointed star), d (4-pointed star), e (rhombus), and f (triangle) (13). Two hepatitis E virus (Paslahepevirus balayani) sequences (genotypes 1 and 3) were used as outgroups. Enlarged area shows sequences from this study and the first 10 most similar sequences from BLAST analysis (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Statistical support values are indicated at nodes; only supports over 70/70 are shown. Scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site.
References
- Palombieri A, Di Profio F, Sarchese V, Fruci P, Suffredini E, Martella V, et al. Surveillance for rat hepatitis E in wastewater networks, Italy. Microbiol Spectr. 2023;11:
e0267523 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Porea D, Raileanu C, Crivei LA, Gotu V, Savuta G, Pavio N. First detection of hepatitis E virus (Rocahepevirus ratti genotype C1) in synanthropic Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in Romania. Viruses. 2023;15:1337. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rivero-Juarez A, Frias M, Perez AB, Pineda JA, Reina G, Fuentes-Lopez A, et al.; HEPAVIR and GEHEP-014 Study Groups. Orthohepevirus C infection as an emerging cause of acute hepatitis in Spain: First report in Europe. J Hepatol. 2022;77:326–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Caballero-Gómez J, Casares-Jiménez M, Gallo-Marín M, Pereira-Pardo S, Beato-Benítez A, Poyato A, et al.; GEHEP-014 Study Group. Rat hepatitis E virus as an aetiological agent of acute hepatitis of unknown origin. J Hepatol. 2025;83:662–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yadav KK, Boley PA, Lee CM, Khatiwada S, Jung K, Laocharoensuk T, et al. Rat hepatitis E virus cross-species infection and transmission in pigs. PNAS Nexus. 2024;3:pgae259. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Rios-Muñoz L, Gonzálvez M, Caballero-Gomez J, Castro-Scholten S, Casares-Jimenez M, Agulló-Ros I, et al. Detection of rat hepatitis E virus in pigs, Spain, 2023. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024;30:823–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Velavan TP, Pallerla SR, Johne R, Todt D, Steinmann E, Schemmerer M, et al. Hepatitis E: An update on One Health and clinical medicine. Liver Int. 2021;41:1462–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fantilli AC, Masachessi G, Cola GD, Castro G, Sicilia P, Marinzalda MLA, et al. Integrated hepatitis e virus monitoring in central Argentina: a six-year analysis of clinical surveillance and wastewater-based epidemiology. Water Res. 2024;261:
122004 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Figueiredo AS, Negreiros IR, do Nascimento E Silva A, Salgado CRS, Dos Santos NL, Pinto MA, et al. Detection of Rocahepevirus ratti in bivalve mollusks from São Luís Island, Maranhão, Brazil: a potential transmission route of an emerging zoonotic pathogen? Food Environ Virol. 2025;17:11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sridhar S, Yip CCY, Wu S, Cai J, Zhang AJX, Leung KH, et al. Rat hepatitis E virus as cause of persistent hepatitis after liver transplant. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018;24:2241–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drexler JF, Seelen A, Corman VM, Fumie Tateno A, Cottontail V, Melim Zerbinati R, et al. Bats worldwide carry hepatitis E virus-related viruses that form a putative novel genus within the family Hepeviridae. J Virol. 2012;86:9134–47. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol. 2021;38:3022–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lo KH, Ho SS, Shun EH, Wu S, Yip CC, Situ J, et al. Enhanced surveillance, subtyping, and host adaptation analysis reveal genotype-wide zoonotic potential of rat hepatitis E virus. J Hepatol. 2026;84:51–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rouba A, Ansmant T, Chaqroun A, Challant J, Josse T, Schvoerer E, et al. First detection of Hepatitis E virus (Rocahepevirus ratti) in French urban wastewater: Potential implications for human contamination. Sci Total Environ. 2024;954:
176805 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Robinson SJ, Borlang J, Himsworth CG, Pearl DL, Weese JS, Dibernardo A, et al. Rat hepatitis E virus in Norway rats, Ontario, Canada, 2018–2021. Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29:1890–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.