Volume 4, Number 4—December 1998
Synopsis
Chlamydia pneumoniae and Cardiovascular Disease
Figure 2
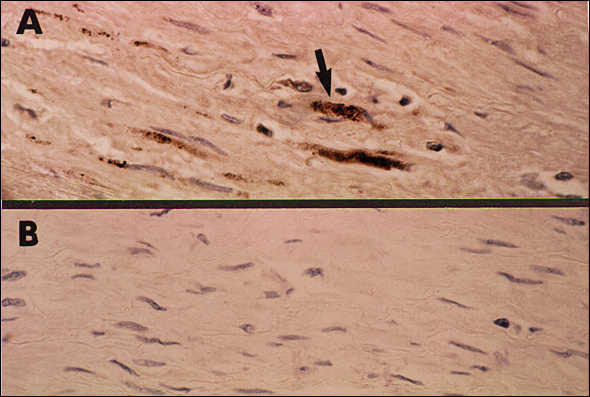
Figure 2. Immunocytochemical staining demonstrating Chlamydia pneumoniae in fibrolipid plaque from coronary artery atheroma. Panel A illustrates positive staining of foam cells in the plaque with the C. pneumoniae—specific monoclonal antibody TT-401. Panel B shows negative staining of the adjacent section using normal ascites fluid as the control.
Page created: December 16, 2010
Page updated: December 16, 2010
Page reviewed: December 16, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.