Volume 4, Number 4—December 1998
Synopsis
Genetic Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases in Humans: Design of Population- Based Studies
Figure 1
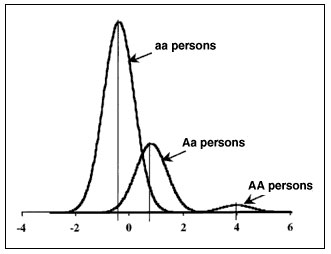
Figure 1. Distribution of the adjusted standardized infection intensities by Schistosoma mansoni predicted by the major gene model obtained from segregation analysis and used for linkage analysis. The frequency of allele A predisposing to high infection levels was estimated at 0.16 (70% of aa, 27% of Aa, and 3% of AA persons), and the three means (corresponding to vertical lines) were -0.43, 0.78, and 3.96 for aa, Aa, and AA persons, respectively, with a residual variance equal to 0.33.
Page created: December 16, 2010
Page updated: December 16, 2010
Page reviewed: December 16, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.