Volume 5, Number 1—February 1999
Dispatch
Mycoplasma penetrans Bacteremia and Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome1
Figure 1
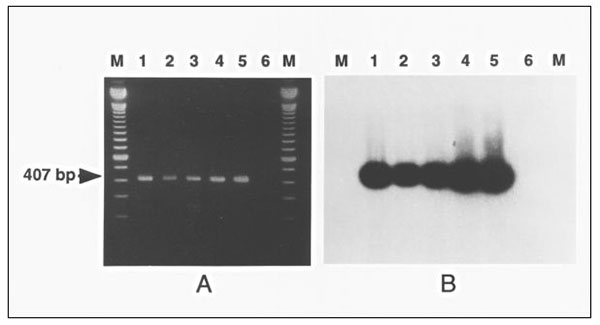
Figure 1. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of Mycoplasma penetrans in clinical samples. A. M. penetrans PCR genomic amplification with the primers MYCPENET-P and MYCPENET-N (7) and analyzed by electrophoresis in 2% agarose gel. Lysates from the following original samples: throat swab (lane 1); tracheal aspirate (lane 2); blood (lane 3); first blood subculture (HF-1 isolate) (lane 4); M. penetrans GTU-54-6A1 (lane 5), showing the amplification product of 407-bp; and negative control (lane 6). B. Southern blotting of the same material. Hybridization with the internal oligonucleotide (MYCPENET-S) probe confirmed the specific amplification of M. penetrans genetic sequences.
References
- Hughes GRV. The antiphospholipid syndrome: ten years on. Lancet. 1993;342:341–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Asherson RA, Cervera R. "Primary," "secondary," and other variants of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 1994;3:293–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Snowden N, Wilson PB, Longson M, Pumphrey RSH. Antiphospholipid antibodies and Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Postgrad Med J. 1990;66:356–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cassell GH, Gray G, Waites KB. Chapter 180: mycoplasmal infections. In: Harrison's principles of internal medicine. Isselbacher KJ, Braunwald E, Wilson JD, Martin JB, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, editors. Vol. 1, McGraw-Hill Inc, 1997:1052-55.
- Lo S-C, Hayes MM, Tully JG, Wang RY-H, Kotani H, Pierce PF, Mycoplasma penetrans sp. nov., from the urogenital tract of patients with AIDS. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992;42:357–64. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Waites KB, Cassell GH, Cannupp KC, Fernandes PB. In vitro susceptibilities of mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas to new macrolides and aryl-fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988;32:1500–2.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grau O, Kovacic R, Griffais R, Launay V, Montagnier L. Development of a PCR-based assays for the detection of two human mollicute species, Mycoplasma penetrans and M. hominis. Mol Cell Probes. 1994;8:139–48. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Blanchard A, Gautier M, Mayau V. Detection and identification of mycoplasmas by amplification of rDNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991;81:37–42.
- Blanchard A, Yáñez A, Watson H, Griffiths G, Cassell GH. Evaluation of intraspecies genetic variation within the 16S rRNA gene of Mycoplasma hominis and detection by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31:1358–61.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grau O, Slizewicz B, Tuppin P, Launay V, Bourgeois E, Sagot N, Association of Mycoplasma penetrans with immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:672–81.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cassell GH, Gambil G, Duffy LB. ELISA in respiratory infections of humans. In: Molecular and diagnostic procedures in mycoplasmology. Vol II. Tully JG, Razin S, editors. Academic Press 1996:123-36.
- Catteau B, Delaporte E, Hachulla E, Piette F, Bergoend H. Infection à mycoplasme avec syndrome de Stevens-Johnson et anticorps antiphospholipides: à propos de deux cas. Rev Med Interne. 1995;16:10–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Presented in part at the 11th International Congress of the International Organization for Mycoplasmology. July 14–19, 1996. Orlando, FL, USA.