Volume 5, Number 3—June 1999
Dispatch
Fatal Case Due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants in an AIDS Patient
Figure 2
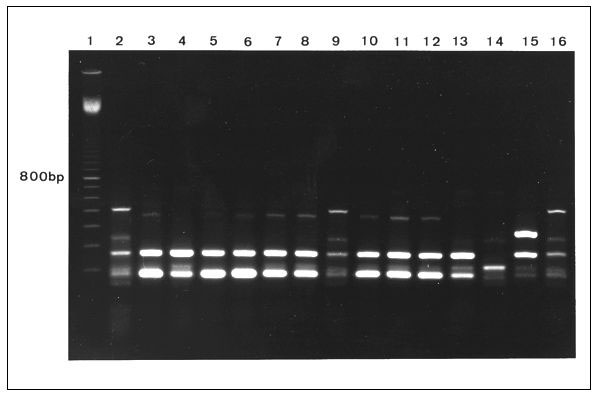
Figure 2. Fingerprint patterns obtained for Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants (lanes 3-5, bloodculture isolates; lanes 6 and 7, isolates from hip abscess; lane 8, postmortem specimen) and S. aureus isolates with a normal phenotype (lanes 10 and 11, isolates from nose and throat; lanes 12 and 13, isolates from hip abscess and postmortem specimen) after polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of inter-IS256 spacer length showing identical strains. Lane 1, 100-bp ladder; lanes 2, 9, and 16, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) reference strain; lanes 14 and 15, epidemiologically unrelated MRSA strains. Strain relatedness of all isolates with different colony morphologies and from different sources was analyzed by PCR analysis of inter-IS256 spacer length polymorphisms (9) and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis after SmaI restriction (8). Minor modifications included the use of brain heart infusion broth instead of trypticase soy broth to obtain sufficient growth of S. aureus small colony variants.
References
- Proctor RA, Balwit JM, Vesga O. Variant subpopulations of Staphylococcus aureus as cause of persistent and recurrent infections. Infect Agents Dis. 1994;3:302–12.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- von Eiff C, Bettin D, Proctor RA, Rolauffs B, Lindner N, Winkelmann W, Recovery of small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus following gentamicin bead placement for osteomyelitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25:1250–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Spearman P, Lakey D, Jotte S, Chernowitz A, Claycomb S, Stratton C. Sternoclavicular joint septic arthritis with small colony variant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996;26:13–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kahl B, Herrmann M, Everding AS, Koch HG, Becker K, Harms E, Persistent infection with small colony variant strains of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:1023–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- von Eiff C, Heilmann C, Proctor RA, Woltz C, Peters G, Götz F. A site-directed Staphylococcus aureus hemB mutant is a small colony variant which persists intracellularly. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:4706–12.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kloos WE, Bannerman TL. Staphylococcus and micrococcus. In: Murray PR, Baron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover FC, Yolken RH, editors. Manual of clinical microbiology. 6th ed. Washington: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. p. 282-98.
- Balwit JM, van Langevelde P, Vann JM, Proctor RA. Gentamicin-resistant menadione and hemin auxotrophic Staphylococcus aureus persist within cultured endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:1033–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Proctor RA, van Langevelde P, Kristjansson M, Maslow JN, Arbeit RD. Persistent and relapsing infections associated with small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:95–102.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Deplano A, Vaneechoutte M, Verschraegen G, Struelens MJ. Typing of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis by PCR analysis of inter-IS256 spacer length polymorphisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:2580–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pelletier LL Jr, Richardson M, Feist M. Virulent gentamicin-induced small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Lab Clin Med. 1979;94:324–34.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Proctor RA, Kahl B, von Eiff C, Vaudaux PE, Lew DP, Peters G. Staphylococcal small colony variants have novel mechanisms for antibiotic resistance. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27(Suppl 1):S68–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar