Volume 7, Number 1—February 2001
Research
Lack of Evidence of Endogenous Avian Leukosis Virus and Endogenous Avian Retrovirus Transmission to Measles Mumps Rubella Vaccine Recipients
Figure 2
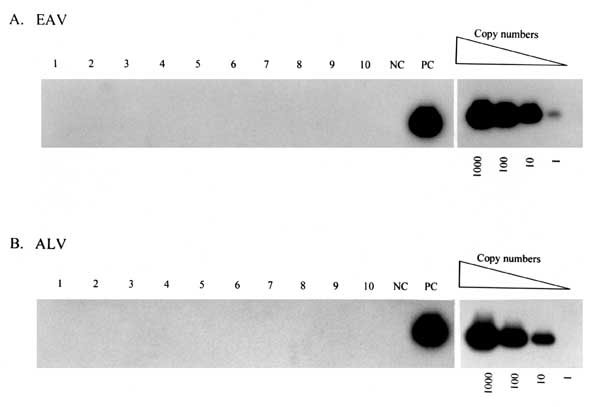
Figure 2. Representative results from polymerase chain reaction analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes from measles mumps rubella (MMR) vaccine recipients for endogenous avian retrovirus (EAV) (A) and avian leukosis virus (ALV) (B) proviral DNA sequences. The detection threshold of known copy numbers of the target sequences is shown in the righthand panels. NC, negative control, uninfected human peripheral blood lymphocytes; PC, positive control, human peripheral blood lymphocytes spiked with 1,000 copies of target sequence; Lanes 1-10, peripheral blood lymphocytes from MMR vaccine recipients.
Page created: March 16, 2011
Page updated: March 16, 2011
Page reviewed: March 16, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.