Volume 8, Number 7—July 2002
Research
Entomologic and Serologic Evidence of Zoonotic Transmission of Babesia microti, Eastern Switzerland
Figure 1
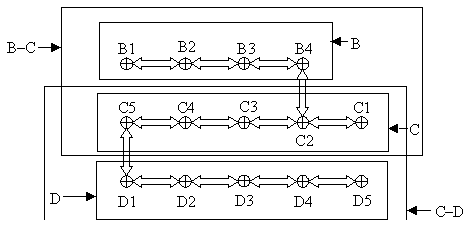
Figure 1. . Schematic drawing of the sampling scheme. Distance between sampling points is 30 m. The letters and solid arrows denote the sections used for prevalence estimation. Sampling lines that connect points not belonging to a section are not included in that section (e.g., line B4–C2 is not part of section B).
Page created: April 19, 2012
Page updated: April 19, 2012
Page reviewed: April 19, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.