Volume 8, Number 7—July 2002
Research
Entomologic and Serologic Evidence of Zoonotic Transmission of Babesia microti, Eastern Switzerland
Figure 2
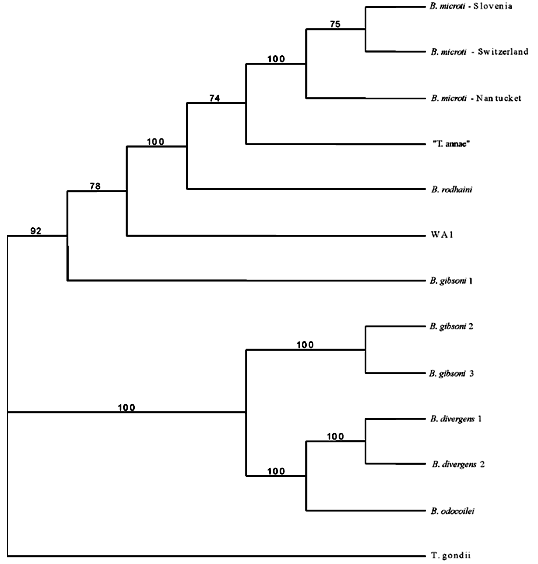
Figure 2. . Maximum parsimony bootstrap consensus tree of 18S rDNA. GenBank accession nos.: Babesia microti-Slovenia AF373332; B. microti-Switzerland AF494286; B. microti- Nantucket AF231348; "Toxoplasma annae" AF188001; B. rodhaini AB049999; WA1 AF158700; B. gibsoni 1 AF158702; B. divergens 1 U07885; B. divergens 2 U16370; B. odocoilei U16369; B. gibsoni 2 AF175300; B. gibsoni 3 AF175301; and Toxoplasma gondii X68523.
Page created: April 19, 2012
Page updated: April 19, 2012
Page reviewed: April 19, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.