Volume 9, Number 11—November 2003
Research
Triosephosphate Isomerase Gene Characterization and Potential Zoonotic Transmission of Giardia duodenalis
Figure 2
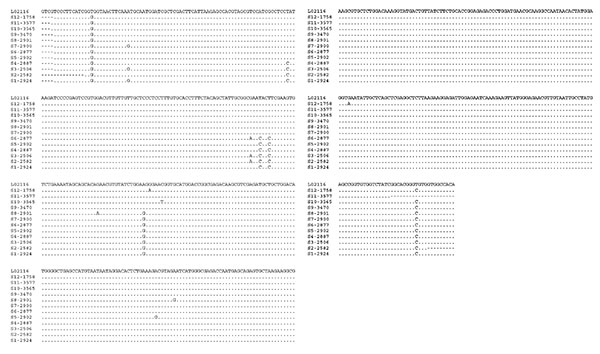
Figure 2. Variation in the triosephosphate isomerase (TPI) nucleotide sequences of G. duodenalis isolates belonging to the assemblage B. Twelve distinct subtypes of G. duodenalis based on the these sequences were evident within assemblage B. The isolates representing these subtypes (S1–S12) as follows: S1 (341, 2578, 2579, 2580, 2586, 2587, 2879, 2890, 2895, 2920, 2924, 2926, 2935, 4599, 4600); S2 (2582, 2583, 2589, 2932); S3 (2506, 2536, 2917); S4 (2590, 2887, 2913, 2915, 2930); S5 (2902); S6 (2877); S7 (2900); S8 (2901); S9 (1653, 1654, 1655, 3469, 3470, 3495, 3500, 3518, 3599); S10 (3565, 3569); S11 (3577); and S12 (1758). Dots denote sequence identity to GenBank accession no. L02116; dashes denote sequence information not obtained.
Page created: January 20, 2011
Page updated: January 20, 2011
Page reviewed: January 20, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.