Volume 9, Number 4—April 2003
Research
Molecular Epidemiology of Human Enterovirus 71 Strains and Recent Outbreaks in the Asia-Pacific Region: Comparative Analysis of the VP1 and VP4 Genes
Figure 5
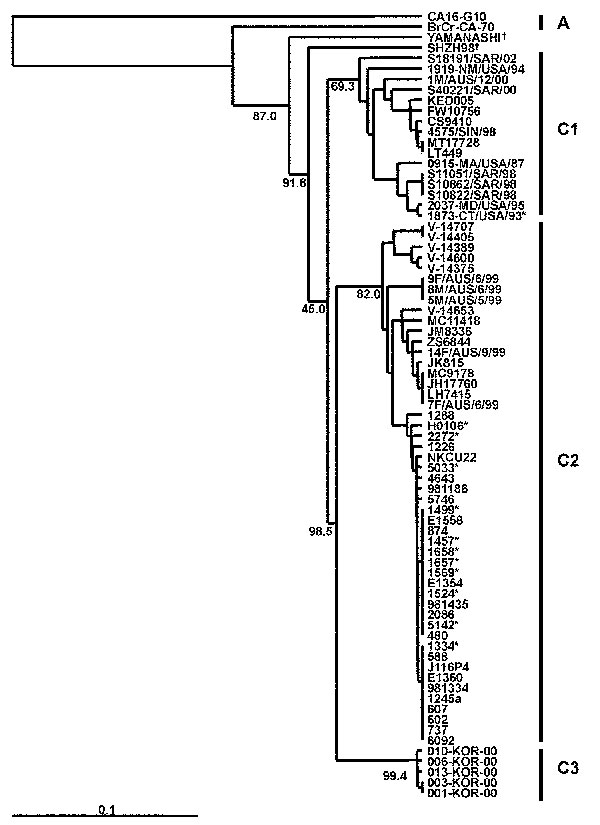
Figure 5. Phylogenetic relationships of human enterovirus 71 (HEV71) strains belonging to genogroup C (21). Dendrogram shows the genetic relationships among 74 HEV71 strains belonging to genogroup C, based on the alignment of the complete VP4 gene sequence (nucleotide positions 744–950). Details of the HEV71 strains included in the dendrogram are provided in Tables 2 and 3. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of nucleotide differences. The bootstrap values in 1,000 pseudoreplicates for major lineages within the dendrogram are shown as percentages. The marker denotes a measurement of relative phylogenetic distance. The VP4 nucleotide sequence of coxsackie virus A16 (29) was used as an outgroup in the analysis. *Denotes HEV71 isolates from fatal cases; †Denotes HEV71 strains falling outside existing genogroup boundaries.
References
- Schmidt NJ, Lennette EH, Ho HH. An apparently new enterovirus isolated from patients with disease of the central nervous system. J Infect Dis. 1974;129:304–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ishimaru Y, Nakano S, Yamaoka K, Takami S. Outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease by enterovirus 71: high incidence of complication disorders of central nervous system. Arch Dis Child. 1980;55:583–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Melnick JL. Enterovirus type 71 infections: a varied clinical pattern sometimes mimicking paralytic poliomyelitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984;6(Suppl 2):S387–90.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alexander JP, Baden L, Pallansch MA, Anderson LJ. Enterovirus 71 infections and neurologic disease—United States, 1977–1991. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:905–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gilbert GL, Dickson KE, Waters MJ, Kennett ML, Land SA, Sneddon M. Outbreak of enterovirus 71 infection in Victoria, Australia, with a high incidence of neurologic involvement. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988;7:484–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Samuda GM, Chang WK, Yeung CY, Tang PS. Monoplegia caused by enterovirus 71: an outbreak in Hong Kong. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987;6:206–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chumakov M, Voroshilova M, Shindarov L, Lavrova I, Gracheva L, Koroleva G, Enterovirus 71 isolated from cases of epidemic poliomyelitis-like disease in Bulgaria. Arch Virol. 1979;60:329–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nagy G, Takatsy S, Kukan E, Mihaly I, Domok I. Virological diagnosis of enterovirus type 71 infections: experiences gained during an epidemic of acute CNS diseases in Hungary in 1978. Arch Virol. 1982;71:217–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chan LG, Parashar UD, Lye MS, Ong FG, Zaki SR, Alexander JP, Deaths of children during an outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Sarawak, Malaysia: clinical and pathological characteristics of the disease. For the Outbreak Study Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31:678–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ho M, Chen ER, Hsu KH, Twu SJ, Chen KT, Tsai SF, An epidemic of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. Taiwan Enterovirus Epidemic Working Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:929–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang JR, Tuan YC, Tsai HP, Yan JJ, Liu CC, Su IJ. Change of major genotype of enterovirus 71 in outbreaks of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Taiwan between 1998 and 2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:10–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lum LC, Wong KT, Lam SK, Chua KB, Goh AY. Neurogenic pulmonary oedema and enterovirus 71 encephalomyelitis. Lancet. 1998;352:1391. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chang LY, Huang YC, Lin TY. Fulminant neurogenic pulmonary oedema with hand, foot and mouth disease. Lancet. 1998;352:367. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cardosa MJ, Krishnan S, Tio PH, Perera D, Wong SC. Isolation of subgenus B adenovirus during a fatal outbreak of enterovirus 71-associated hand, foot, and mouth disease in Sibu, Sarawak. Lancet. 1999;354:987–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shimizu H, Utama A, Yoshii K, Yoshida H, Yoneyama T, Sinniah M, Enterovirus 71 from fatal and nonfatal cases of hand, foot and mouth disease epidemics in Malaysia, Japan and Taiwan in 1997–1998. Jpn J Infect Dis. 1999;52:12–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang JR, Tsai HP, Chen PF, Lai YJ, Yan JJ, Kiang D, An outbreak of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan, 1998. II. Laboratory diagnosis and genetic analysis. J Clin Virol. 2000;17:91–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shih SR, Ho MS, Lin KH, Wu SL, Chen YT, Wu CN, Genetic analysis of enterovirus 71 isolated from fatal and non-fatal cases of hand, foot and mouth disease during an epidemic in Taiwan, 1998. Virus Res. 2000;68:127–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh S, Chow VT, Chan KP, Ling AE, Poh CLRT-PCR. nucleotide, amino acid and phylogenetic analyses of enterovirus type 71 strains from Asia. J Virol Methods. 2000;88:193–204. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chu PY, Lin KH, Hwang KP, Chou LC, Wang CF, Shih SR, Molecular epidemiology of enterovirus 71 in Taiwan. Arch Virol. 2001;146:589–600. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- AbuBakar S, Chee HY, Al-Kobaisi MF, Xiaoshan J, Chua KB, Lam SK. Identification of enterovirus 71 isolates from an outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) with fatal cases of encephalomyelitis in Malaysia. Virus Res. 1999;61:1–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brown BA, Oberste MS, Alexander JP Jr, Kennett ML, Pallansch MA. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of enterovirus 71 strains isolated from 1970 to 1998. J Virol. 1999;73:9969–75.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- McMinn P, Lindsay K, Perera D, Chan HM, Chan KP, Cardosa MJ. Phylogenetic analysis of enterovirus 71 strains isolated during linked epidemics in Malaysia, Singapore, and Western Australia. J Virol. 2001;75:7732–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chan KP, Goh KT, Chong CY, Teo ES, Lau G, Ling AE. Epidemic hand, foot and mouth disease caused by human enterovirus 71, Singapore. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:78–85.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brown BA, Kilpatrick DR, Oberste MS, Pallansch MA. Serotype-specific identification of enterovirus 71 by PCR. J Clin Virol. 2000;16:107–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Felsenstein J. PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (version 3.5). Cladistics. 1989;5:164–6.
- Page RD. TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci. 1996;12:357–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Genetics Computer Group. Program manual for the Wisconsin GCG package. 8.0 1994 ed. Madison (WI): Genetics Computer Group; 1994
- Poyry T, Hyypia T, Horsnell C, Kinnunen L, Hovi T, Stanway G. Molecular analysis of coxsackie virus A16 reveals a new genetic group of enteroviruses. Virology. 1994;202:982–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brown BA, Pallansch MA. Complete nucleotide sequence of enterovirus 71 is distinct from poliovirus. Virus Res. 1995;39:195–205. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stanway G, Hovi T, Knowles NJ, Hyypia T. Molecular and biological basis of Picornavirus taxonomy. In: Semler BL, Wimmer E, editors. Molecular biology of picornaviruses. Washington: ASM Press; 2002. p. 17–24.
- Oberste MS, Maher K, Kilpatrick DR, Pallansch MA. Molecular evolution of the human enteroviruses: correlation of serotype with VP1 sequence and application to picornavirus classification. J Virol. 1999;73:1941–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rossman MG, Arnold A, Erickson JW, Frankenberger EA, Griffith JP, Hecht HJ, Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985;317:145–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar