Volume 9, Number 7—July 2003
Research
Mutations in Putative Mutator Genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strains of the W-Beijing Family
Figure 2
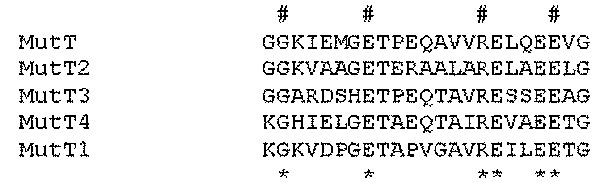
Figure 2. MutT proteins’ sequences alignment. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2985(MutT1), Rv1160(MutT2), Rv0413(MutT3), and Rv3908(MutT4) were selected from the M. tuberculosis genome because of their annotation or after a BLAST analysis. These sequences were compared to Escherichia coli mutT by using alignments available from: http://www.biochem.uthscsa.edu/~barnes/mutt.html. The detected region of similarity is shown here. #, absolutely conserved residues; *, residues that are strongly conserved and that define the mutT or nudix motif.
Page created: December 22, 2010
Page updated: December 22, 2010
Page reviewed: December 22, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.