Volume 9, Number 9—September 2003
Research
Human Metapneumovirus Detection in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
Figure 4
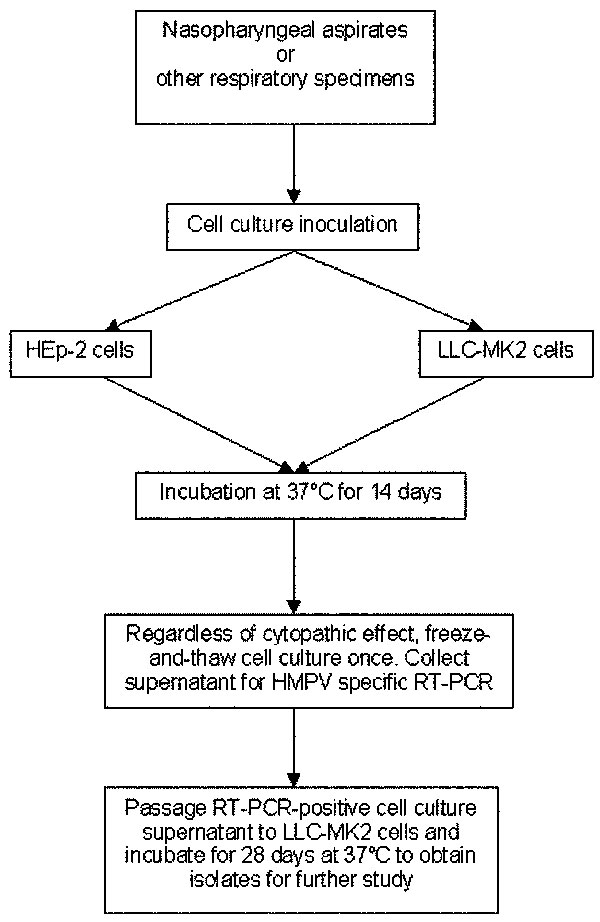
Figure 4. Combination approach of conventional virus isolation and molecular techniques to detect human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infection. Nasopharyngeal aspirates were examined in this study. This approach can be applied to other respiratory specimens. Prolonged incubation of rhesus monkey kidney (LLC-MK2) cells to 28 days for culture of original specimens may improve sensitivity of detection. Detection based on cytopathic effect is not sensitive for first-round culture from original specimens. All cell cultures should be examined by HMPV–specific reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
Page created: January 03, 2011
Page updated: January 03, 2011
Page reviewed: January 03, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.