Volume 9, Number 9—September 2003
Research
Human Metapneumovirus Detection in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
Figure 1
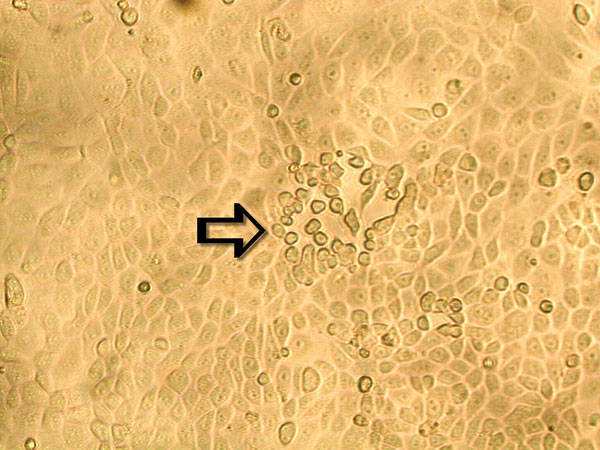
Figure 1. Early cytopathic effect of human metapneumovirus in rhesus monkey kidney (LLC-MK2) cell monolayers. A focus of infected cells that exhibit refractile rounding is indicated by an arrow (100X).
Page created: January 03, 2011
Page updated: January 03, 2011
Page reviewed: January 03, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.