Volume 10, Number 2—February 2004
THEME ISSUE
2004 SARS Edition
Laboratory Study
Ultrastructural Characterization of SARS Coronavirus
Figure 3
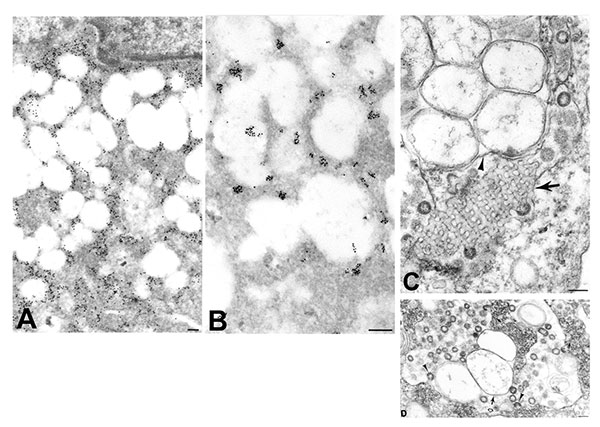
Figure 3. Ultrastructural characteristics of double-membrane vesicles. A) Immunogold labeling of viral proteins by using hyperimmune mouse ascitic fluid (12 nm gold) in areas of cytoplasm in close proximity to the double-membrane vesicles. B) Ultrastructural in situ hybridization detection of viral mRNA, genRNA, or both (6 nm gold) in the same areas and also at times associated with diffuse granular material within the double-membrane vesicles. C) Double-membrane vesicles showing several single-membrane vesicles enclosed within an outer membrane (arrowhead). Also present is a tubuloreticular structure (arrow) with virus particles budding from the membranes. D) Double-membrane vesicles with a large space between the inner (arrow) and outer (open arrow) membranes of the vesicles. Virions are seen budding into (arrowheads) and accumulating within the dilated inter-membrane space. At the periphery of the double-membrane vesicles are nucleocapsid inclusions; arrows point to discernable nucleocapsids (small arrows). Bars, 100 nm.