Volume 10, Number 5—May 2004
Research
Causative Agent of Pogosta Disease Isolated from Blood and Skin Lesions
Figure 2
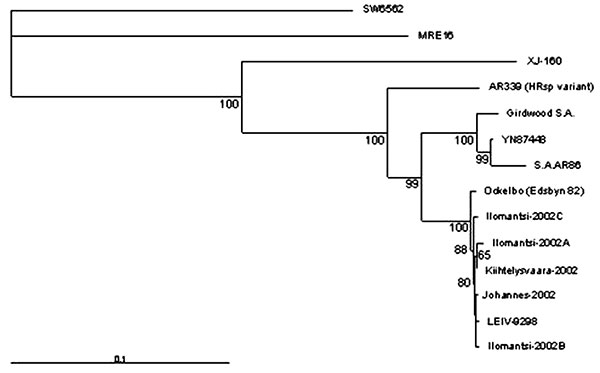
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree is based on the nucleotide sequences of 1,178–1,281 bp from nsP3 and nsP4 region, nucleotides 5,258-6,510; the genome position is given according to the published sequence of the strain AR339 (HRsp variant) (2). The tree was constructed by using Neighbor-joining algorithms (NEIGHBOR). 5,000 bootstrap replicates were calculated. Only those bootstrap support values that exceed 50% are shown. The following sequences available in GenBank were included into the comparison: AR339 (HRsp variant); Egypt (J02363, J02364, J02365, J02366, J02367), Girdwood S.A.; South-Africa (U38304), MRE16; Malaysia (AF492770), Ockelbo (Edsbyn 82); Sweden (M69205), S.A.AR86; South-Africa (U38305), SW6562; Australia (AF429428), YN87448; China (AF103734) and XJ-160; China (AF103728).
References
- Taylor RM, Hurlbut HS, Work TH, Kingsbury JR, Frothingham TE. Sindbis virus: a newly recognized arthropod-transmitted virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1955;4:844–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Strauss EG, Rice CM, Strauss JH. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1984;133:92–110. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brummer-Korvenkontio M, Vapalahti O, Kuusisto P, Saikku P, Manni T, Koskela P, Epidemiology of Sindbis virus infections in Finland 1981–96: possible factors explaining a peculiar disease pattern. Epidemiol Infect. 2002;129:335–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Turunen M, Kuusisto P, Uggeldahl PE, Toivanen A. Pogosta disease: clinical observations during an outbreak in the province of North Karelia, Finland. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37:1177–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lvov DK, Vladimirtseva EA, Butenko AM, Karabatsos N, Trent DW, Calisher CH. Identity of Karelian fever and Ockelbo viruses determined by serum dilution-plaque reduction neutralization tests and oligonucleotide mapping. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988;39:607–10.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lvov DK, Skvortsova TM, Berezina LK, Gromashevsky VL, Yakovlev BI, Gushchin BV, Isolation of Karelian fever agent from Aedes communis mosquitoes. Lancet. 1984;2:399–400. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shirako Y, Niklasson B, Dalrymple JM, Strauss EG, Strauss JH. Structure of the Ockelbo virus genome and its relationship to other Sindbis viruses. Virology. 1991;182:753–64. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Skogh M, Espmark A. Ockelbo disease: epidemic arthritis-exanthema syndrome in Sweden caused by Sindbis-virus like agent. Lancet. 1982;1:795–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lundstrom JO, Vene S, Espmark A, Engvall M, Niklasson B. Geographical and temporal distribution of Ockelbo disease in Sweden. Epidemiol Infect. 1991;106:567–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Niklasson B, Espmark Å, LeDuc JW, Gargan TP, Ennis WA, Tesh RB, Association of a Sindbis-like virus with Ockelbo disease in Sweden. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984;33:1212–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lundström JO, Lindström KM, Olsen B, Dufva R, Krakower DS. Prevalence of Sindbis virus neutralizing antibodies among Swedish passerines indicates that thrushes are the main amplifying hosts. J Med Entomol. 2001;38:289–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lundström JO, Turell MJ, Niklasson B. Viremia in three orders of birds (Anseriformes, Galliformes and Passeriformes) inoculated with Ockelbo virus. J Wildl Dis. 1993;29:189–95.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Malherbe H, Strickland-Cholmley M, Jackson AL. Sindbis virus infection in man. Report of a case with recovery of virus from skin lesions. S Afr Med J. 1963;37:547–52.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhou G, Liang G, Li L. Complete nucleotide sequence of the nonstructural gene of alphavirus YN87448 strain isolated in China and its relationship to other Sindbis viruses. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 1999;13:314–20.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hörling J, Vene S, Franzen C, Niklasson B. Detection of Ockelbo virus RNA in skin biopsies by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31:2004–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vene S, Franzen C, Niklasson B. Development of specific antibody patterns and clinical symptoms following Ockelbo virus infection. Arch Virol. 1994;134:61–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Niklasson B, Espmark A, Lundstrom J. Occurrence of arthralgia and specific IgM antibodies three to four years after Ockelbo disease. J Infect Dis. 1998;157:832–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Heise MT, Simpson DA, Johnston RE. Sindbis-group alphavirus replication in periosteum and endosteum of long bones in adult mice. J Virol. 2000;74:9294–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Luukkainen R, Laine M, Nirhamo J. Chronic arthritis after Sindbis-related (Pogosta) virus infection. Scand J Rheumatol. 2000;29:399–400. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Autio P, Niemi KM, Kariniemi AL. An eruption associated with alphavirus infection. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:320–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mackenzie JS, Lindsay MD, Coelen RJ, Broom AK, Hall RA, Smith DW. Arboviruses causing human disease in the Australasian zoogeographic region. Arch Virol. 1994;136:447–67. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Doherty RL, Bodey AS, Carew JS. Sindbis virus infection in Australia. Med J Aust. 1969;2:1016–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guard RW, McAuliffe MJ, Stallman ND, Bramston BA. Haemorrhagic manifestations with Sindbis infection. Case report. Pathology. 1982;14:89–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boughton CR, Hawkes RA, Naim HM, Wild J, Chapman B. Arbovirus infections in humans in New South Wales. Seroepidemiology of the alphavirus group of togaviruses. Med J Aust. 1984;141:700–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Norder H, Lundstrom JO, Kozuch O, Magnius LO. Genetic relatedness of Sindbis virus strains from Europe, Middle East, and Africa. Virology. 1996;222:440–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Buckley A, Dawson A, Moss SR, Hinsley SA, Bellamy PE, Gould EA. Serological evidence of West Nile virus, Usutu virus and Sindbis virus infection of birds in the UK. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:2807–17. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sammels LM, Lindsay MD, Poidinger M, Coelen RJ, Mackenzie JS. Geographic distribution and evolution of Sindbis virus in Australia. J Gen Virol. 1999;80:739–48.PubMedGoogle Scholar