Volume 10, Number 7—July 2004
Research
Recombinant Viruses and Early Global HIV-1 Epidemic
Figure 1
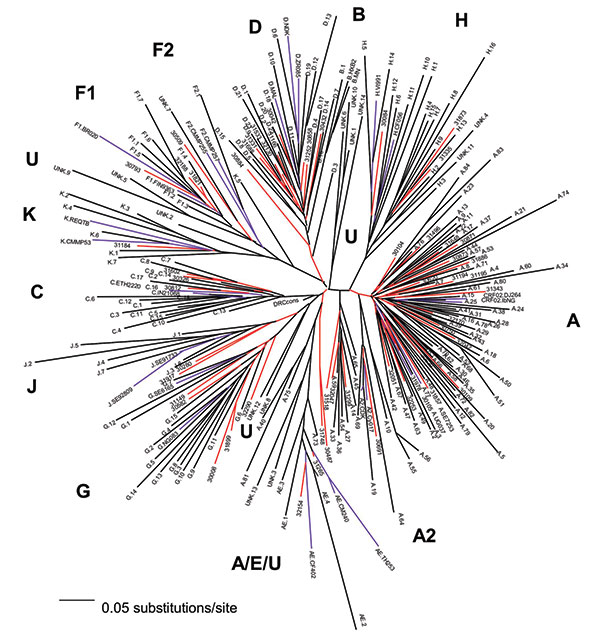
Figure 1. Neighbor-joining tree of 56 Zaire strains from the mid-1980s, 197 Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) strains from 1997, and subtype-specific reference strains. The number of nucleotides in the final alignment was 304 bp after gap stripping. The model of evolutionary change used in the tree was the Transversional Model (TVM) +g (0.8575), where g is the shape parameter of the γ distribution (heterogeneity among sites) and TVM is the model of substitution whereby A↔G = C↔T and the other four rates, all transversions, are unique. Our 1980s C2V3C3 sequences are indicated by a five-digit code, and their branches are red; the 1997 sequences have the subtype (as indicated in GenBank) as the first letter, followed by a one- or two-digit number or the designation unk = unclassifiable, and these branches are black; the reference strains have the subtype as the first letter followed by the reference name as follows: A.SE7253, A.92UG037, A2.CDK, A2.Cy017; B.HXB2, B.MN; C.ETH2220, C.IN21068; D.84ZR085, D.NDK, MAL; E.CD402, E.CM240, E.TH253; F1.FIN9363, F1.93BR020; F2.CMMP255, F2.CMMP257, G.NG083, G.SE6165; H.90CF056, H.VI991, J.SE91733, J.SE92809; K.96CMMP253, and K.97REQTB; these branches are purple. Subtype characterizations of the phylogenetic clusters in the tree are indicated in bold, lineages consisting of unclassifiable sequences are designated as U.