Volume 13, Number 10—October 2007
Research
Evolutionary Relationships between Bat Coronaviruses and Their Hosts
Figure 1
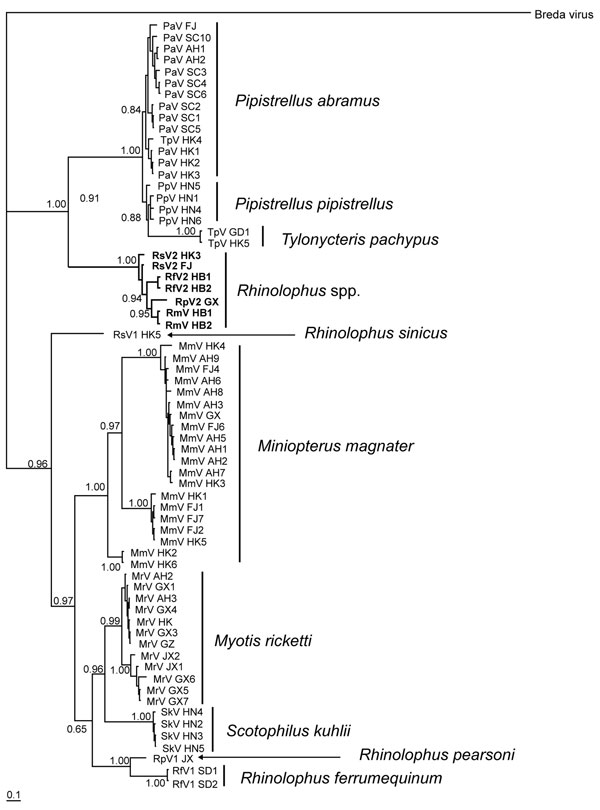
Figure 1. Phylogram of bat coronaviruses based on the 440-bp RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene region. Methods used are described in the text. Values to the left of branches are Bayesian posterior probabilities. Scale bar at the lower left indicated 0.1 nucleotide substitutions per site. Boldface branches indicate severe acute respiratory syndrome–like coronaviruses, and species names to the right of lineages indicate putative reservoir host(s). Pa, Pipistrellus abramus; Tp, Tylonycteris pachypus; Pp, P. pipistrellus; Rs, Rhinolophus sinicus; Rf, R. ferrumequinum; Rp, R. pearsoni; Rm, R. macrotis; Mm, Miniopterus magnater; Mr, Myotis ricketti; Sk, Scotophilus kuhlii. Sequences obtained from GenBank were as follows: DQ412043 isolated from R. macrotis in Hubei Province (HB); DQ412042 isolated from R. ferrumequinum in HB; DQ071615 isolated from R. pearsoni in Guangxi Province (GX); DQ022305, DQ084199, DQ084200, DQ249213, and DQ249235 isolated from R. sinicus in Hong Kong (HK); DQ249214, DQ249215, DQ249216, DQ249217, and DQ074652 isolated from T. pachypus in HK; DQ249218, DQ249219, and DQ249221 isolated from Pipistrellus abramus in HK; DQ249224 isolated from Myotis ricketti in HK; and DQ249226, DQ666337, DQ666339, DQ666340, DQ249228, and DQ666338 isolated from M. magnater in HK. FJ, Fujian Province; SC, Sichuan Province; AH, Anhui Province; HN, Hainan Province; GD, Guandong Province; JX, Jiangxi Province; SD, Shandong Province.