Volume 13, Number 10—October 2007
Research
Evolutionary Relationships between Bat Coronaviruses and Their Hosts
Figure 3
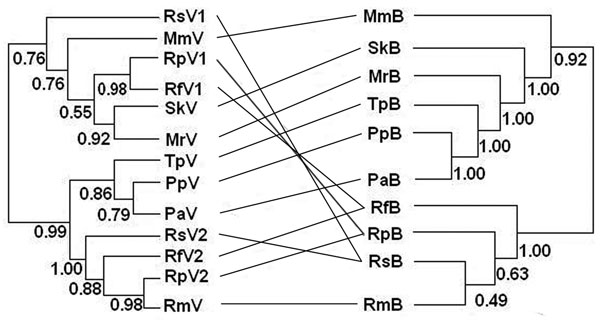
Figure 3. Phylogenetic relationships between coronaviruses (left) and their host bat species added for reference (right). Abbreviations on both sides denote viruses harbored by bats (marked as V on the left) and bats (marked as B on the right). Rs, Rhinolophus sinicus; Mm, Miniopterus magnater; Sk, Scotophilus kuhlii; Rp, R. pearsoni; Mr, Myotis ricketti; Rf, R. ferrumequinum; Tp, Tylonycteris pachypus; Pp, Pipistrellus pipistrellus; Pa, P. abramus; Rm, R. macrotis. Values below branches are Bayesian posterior probabilities. Although some of these values are low, our analysis demonstrated a pathway for future study (28). Lines between the 2 trees were added to help visualize virus and host sequence congruence or incongruence.
References
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Bercker S, Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kuiken T, Fouchier RA, Schutten M, Rimmelzwaan GF, van Amerongen G, van Riel D, Newly discovered coronavirus as the primary cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2003;362:263–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guan Y, Zheng BJ, He YQ, Liu XL, Zhuang ZX, Cheung CL, Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science. 2003;302:276–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van der Hoek L, Pyrc K, Jebbink MF, Vermeulen-Oost W, Berkhout RJ, Wolther KC, Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat Med. 2004;10:368–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Chu CM, Chan KH, Tsoi HW, Huang Y, Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J Virol. 2005;79:884–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li W, Shi Z, Yu M, Ren W, Smith C, Epstein JH, Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses. Science. 2005;310:676–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lau SK, Woo PC, Li KS, Huang Y, Tsoi HW, Wong BH, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:14040–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Simmons NB. Order Chiroptera. In: Wilson DE, Reeder DM, editors. Mammal species of the world. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; 2005. p. 312–529.
- Poon LL, Chu DK, Chan KH, Wong OK, Ellis TM, Leung YH, Identification of a novel coronavirus in bats. J Virol. 2005;79:2001–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tang XC, Zhang JX, Zhang SY, Wang P, Fan XH, Li LF, Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. J Virol. 2006;80:7481–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Li KS, Poon RW, Wong BH, Tsoi HW, Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats. Virology. 2006;351:180–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chu DK, Poon LL, Chan KH, Chen H, Guan Y, Yuen KY, Coronaviruses in bent-winged bats (Miniopterus spp.). J Gen Virol. 2006;87:2461–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lukashov VV, Goudsmit J. Evolutionary relationships among parvoviruses: virus-host coevolution among autonomous primate parvoviruses and links between adeno-associated and avian parvoviruses. J Virol. 2001;75:2729–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kariwa H. Bunyavirus virus and host relationship: the coevolution between hantavirus and rodent. Uirsu. 2002;52:61–7.
- Herniou EA, Olszewski JA, O’Reilly DR, Cory JS. Ancient coevolution of baculoviruses and their insect hosts. J Virol. 2004;78:3244–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Perez-Losada M, Christensen RG, McClellan DA, Adams BJ, Viscidi RP, Demma JC, Comparing phylogenetic codivergence between polyomaviruses and their hosts. J Virol. 2006;80:5663–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Page RD. Parallel phylogenies: reconstructing the history of host-parasite assemblages. Cladistics. 1994;10:155–73. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Antonovics J, Hood M, Partain J. The ecology and genetics of a host shift: Microbotryum as a model system. Am Nat. 2002;160:S40–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen H, Smith G, Li KS, Wang J, Fan XH, Rayner JM, Establishment of multiple sublineages of H5N1 influenza virus in Asia: implications for pandemic control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:2845–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li G, Jones G, Rossiter SJ, Chen S, Parson S, Zhang S. Phylogenetics of small horseshoe bats from East Asia based on mitochondrial DNA sequence variation. J Mammal. 2006;87:1234–40. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Irwin DM, Kocher TD, Wilson AC. Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J Mol Evol. 1991;32:128–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmouqin F, Higgins DG. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:4876–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:754–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 2004;5:150–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Posada D, Crandall KA. Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:817–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swofford DL. PAUP* beta version: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2002.
- Nei M. Molecular evolutionary genetics. New York: Columbia University Press; 1987.
- Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S. Arlequin ver. 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online. 2005;1:47–50.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller-Butterworth CM, Jacobs DS, Harley EH. Strong population substructure is correlated with morphology and ecology in a migratory bat. Nature. 2003;424:187–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Holmes EC. Error thresholds and the constraints to RNA virus evolution. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:543–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dobson AP. What links bats to emerging infectious diseases? Science. 2005;310:628–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:531–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vijaykrishna D, Smith GJ, Zhang JX, Peiris JS, Chen H, Guan Y. Evolutionary insights into the ecology of coronaviruses. J Virol. 2007;81:4012–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Saif LJ. Animal coronaviruses: what can they teach us about the severe acute respiratory syndrome? Rev Sci Tech. 2004;23:643–60.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burke DS. The evolvability of emerging viruses. In: Nelson AM, Horsburgh CR, editors. Pathology of emerging infections. Washington: American Society for Microbiology; 1998. p. 1–12.
- Dominguez SR, O’Shea TJ, Oko LM, Holmes KV. Detection of group 1 coronaviruses in bats in North America. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1295–300.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Müller MA, Paweska JT, Leman PA, Drosten C, Grywna K, Kemp A, Coronavirus antibodies in African bat species. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1367–70.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: July 02, 2010
Page updated: July 02, 2010
Page reviewed: July 02, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.