Volume 13, Number 3—March 2007
Research
Matrix Protein 2 Vaccination and Protection against Influenza Viruses, Including Subtype H5N1
Figure 4
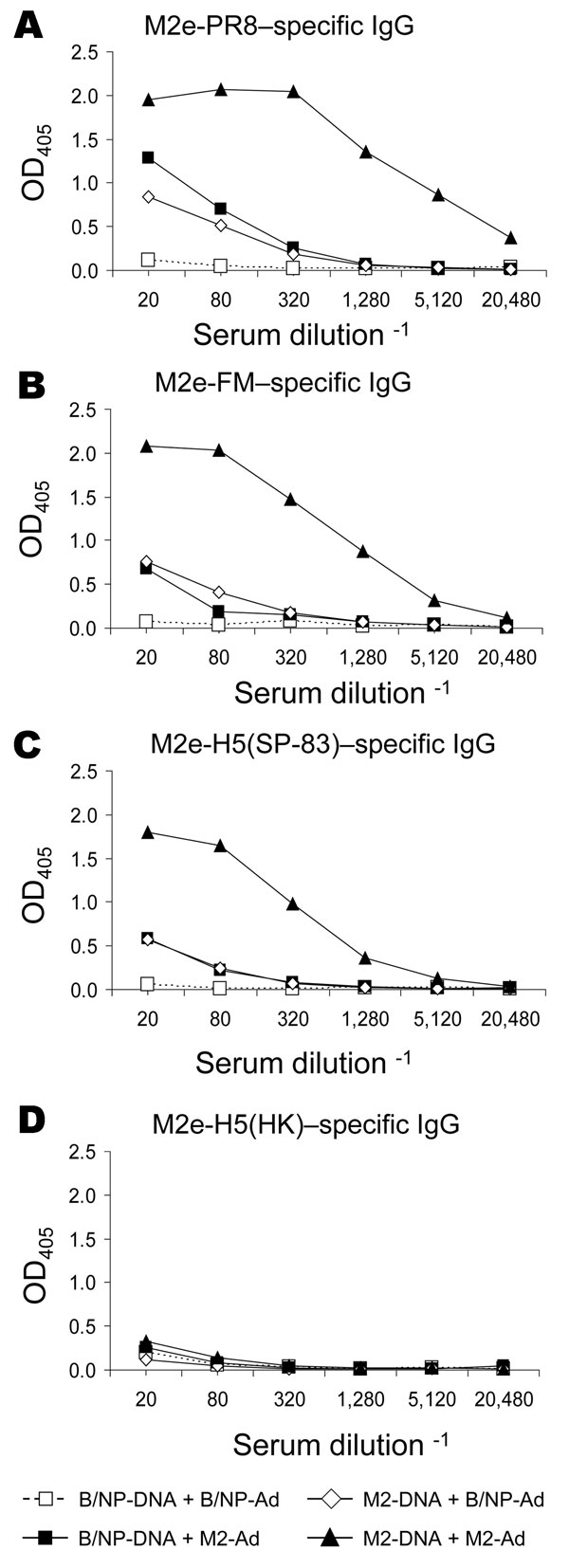
Figure 4. Results of matrix protein 2 (M2) vaccination and booster with DNA prime–adenovirus (Ad), showing cross-reactive antibodies. Mice (8–10 per group) were vaccinated with DNA and given an Ad booster as described in Methods. Immune serum collected 3 weeks after the booster was assayed for immunoglobulin (Ig) G reactive to various M2e peptides by ELISA, as described in Methods. Plates were coated with M2e-PR8 (panel A), M2e-FM (panel B), M2e-H5(SP-83) (panel C), or M2e-H5(HK) (panel D). OD, optical density.
Page created: June 29, 2010
Page updated: June 29, 2010
Page reviewed: June 29, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.