Volume 13, Number 9—September 2007
Dispatch
Mokola Virus in Domestic Mammals, South Africa
Figure
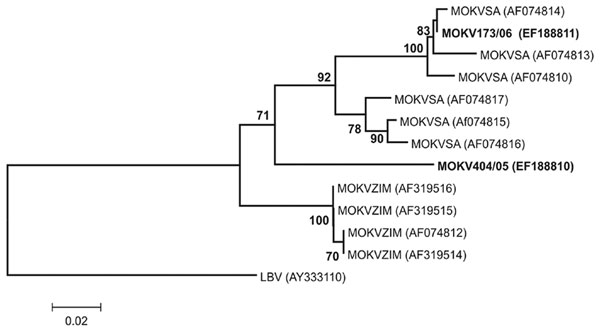
Figure. Phylogenetic tree based on 267 nt of partial nucleoprotein gene sequences of Moloka virus (MOKV) identified with the N1-N2 primer set as described (12). The tree shows phylogenetic positions of 2 recently identified cases of MOKV infection from South Africa (MOKV173/06 from a cat and MOKV404/05 from a dog) (in boldface) relative to previously characterized MOKV isolates from South Africa (SA) and Zimbabwe (ZIM) and Lagos bat virus (LBV) as the outgroup. GenBank accession nos. are shown in parenthesis. Bootstrap support values >70% are considered significant and indicated. Scale bar shows nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA. Virus taxonomy: the classification and nomenclature of viruses. The eighth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. San Diego: Academic Press; 2004. p. 623–31.
- Shope RE, Murphy FA, Harrison AK, Causey OR, Kemp GE, Simpson DI, Two African viruses serologically and morphologically related to rabies virus. J Virol. 1970;6:690–2.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kemp GE, Causey OR, Moore DL, Odelola A, Fabiyi A. Mokola virus. Further studies on IbAn 27377, a new rabies-related etiologic agent of zoonosis in Nigeria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1972;21:356–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Familusi JB, Osunkoya BO, Moore DL, Kemp GE, Fabiyi A, Moore DL. A fatal human infection with Mokola virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1972;21:959–63.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Gonidec G, Rickenbach A, Robin Y, Heme G. Isolation of a strain of Mokola virus in Cameroon. Ann Microbiol (Paris). 1978;129:245–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Saluzzo JF, Rollin PE, Daugard C, Digoutte JP, Georges AJ, Sureau P. Premier isolement du virus Mokola a partir d’une rongeur (Lophuromys sikapusi). Ann Inst Pasteur Virol. 1984;135E:57–66. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Foggin CM. Rabies and rabies-related viruses in Zimbabwe: historical, virological and ecological aspects [doctoral dissertation]. Harare (Zimbabwe): University of Zimbabwe; 1988.
- Mebatsion T, Cox JH, Frost JW. Isolation and characterisation of 115 street rabies virus isolates from Ethiopia by using monoclonal antibodies: identification of 2 isolates of Mokola and Lagos bat viruses. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:972–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meredith CD, Nel LH, von Teichman BF. A further isolation of Mokola virus in South Africa. Vet Rec. 1996;138:119–20.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- von Teichman BF, de Koker WC, Bosch SJ, Bishop GC, Meredith CD, Bingham J. Mokola virus infection: description of recent South African cases and a review of the virus epidemiology. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 1998;69:169–71.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bingham J, Javangwe S, Sabeta CT, Wandeler AI, Nel LH. Report of isolations of unusual lyssaviruses (rabies and Mokola virus) identified retrospectively from Zimbabwe. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2001;72:92–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nel L, Jacobs J, Jaftha J, von Teichman B, Bingham J. New cases of Mokola virus infection in South Africa: a genotypic comparison of Southern African virus isolates. Virus Genes. 2000;20:103–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Paweska JT, Blumberg LH, Liebenberg C, Hewlett RH, Grobelaar AA, Leman PA, Fatal human infection with rabies-related Duvenhage virus, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1965–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Markotter W, Randles J, Rupprecht CE, Sabeta CT, Taylor PJ, Wandeler AI, Lagos bat virus, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:504–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Markotter W, Kuzmin I, Rupprecht CE, Randles J, Sabeta CT, Wandeler AI, Isolation of Lagos bat virus from water mongoose. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1913–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: July 01, 2010
Page updated: July 01, 2010
Page reviewed: July 01, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.