Volume 14, Number 1—January 2008
Research
Cross-subtype Immunity against Avian Influenza in Persons Recently Vaccinated for Influenza
Figure 1
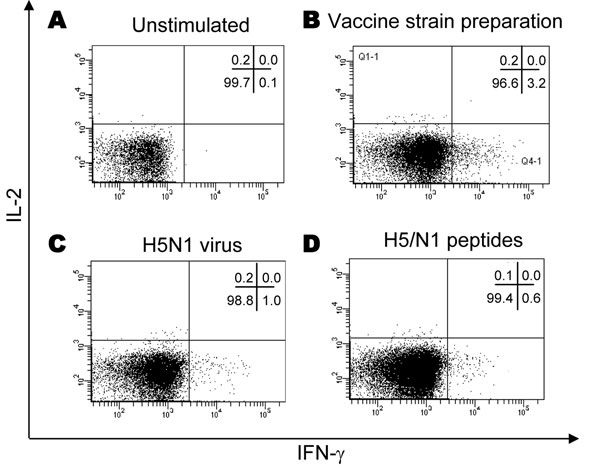
Figure 1. Detection of antigen-specific CD4 T cells against influenza viruses by flow cytometry after in vitro expansion of effector cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were expanded in vitro with interleukin-2 (IL-2) for 9 days in the presence or absence of specific influenza antigens, as indicated, then analyzed by flow cytometry by using the intracellular staining assay. The effector T-cell response was analyzed for interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) or IL-2 cytokine expression. Unstimulated cultures (A), CD4 T-cell response against human influenza vaccine strain preparation (B), inactivated avian influenza (H5N1) (C), and H5/N1 peptides (D) are shown in a representative donor.
Page created: July 07, 2010
Page updated: July 07, 2010
Page reviewed: July 07, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.