Volume 14, Number 11—November 2008
Dispatch
Novel Human Rhinoviruses and Exacerbation of Asthma in Children1
Figure
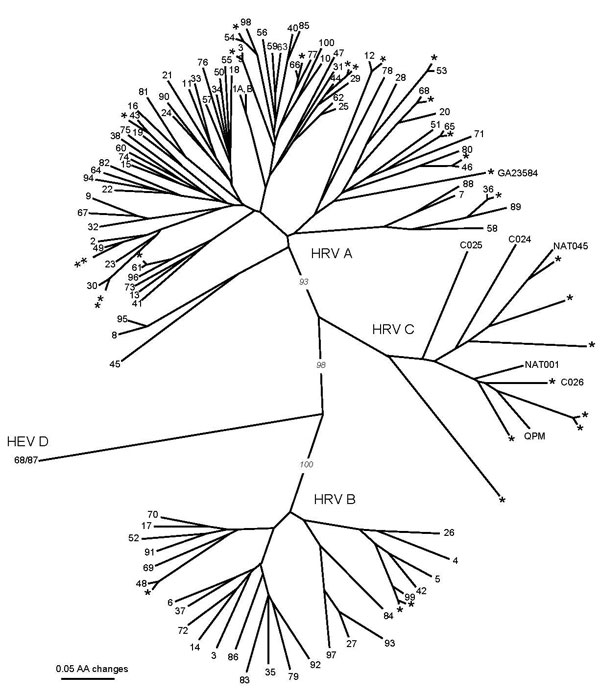
Figure. Phylogenetic tree of partial virus capsid protein 1 (VP1) amino acid sequences of human rhinoviruses (HRVs) identified in 29 HRV-positive pediatric asthma patients, March 2003–February 2004, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (designated *), previously published sequences of strains QPM (GenBank accession no. EF186077), C024-C026 (accession nos. EF582385–EF582387), and NAT001 and NAT045 (accession nos. EF077279–EF077280). HRV prototype strains designated 1A, 1B, 2-100. Human enterovirus (HEV) 68/HRV87 (designated 68/87) is included as outgroup. Tree construction and bootstrap values determined with PAUP* (11).
References
- Gern JE, Busse WW. Association of rhinovirus infections with asthma. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12:9–18.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ledford RM, Patel NR, Demenczuk TM, Watanyar A, Herbertz T, Collett MS, VP1 sequencing of all human rhinovirus serotypes: insights into genus phylogeny and susceptibility to antiviral capsid-binding compounds. J Virol. 2004;78:3663–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Laine P, Savolainen C, Blomqvist S, Hovi T. Phylogenetic analysis of human rhinovirus capsid protein VP1 and 2A protease coding sequences confirms shared genus-like relationships with human enteroviruses. J Gen Virol. 2005;86:697–706. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McErlean P, Shackelton LA, Lambert SB, Nissen MD, Sloots TP, Mackay IM. Characterisation of a newly identified human rhinovirus, HRV-QPM, discovered in infants with bronchiolitis. J Clin Virol. 2007;39:67–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lamson D, Renwick N, Kapoor V, Liu Z, Palacios G, Ju J, MassTag polymerase-chain-reaction detection of respiratory pathogens, including a new rhinovirus genotype, that caused influenza-like illness in New York State during 2004–2005. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:1398–402. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lau SK, Yip CC, Tsoi HW, Lee RA, So LY, Lau YL, Clinical features and complete genome characterization of a distinct human rhinovirus (HRV) genetic cluster, probably representing a previously undetected HRV species, HRV-C, associated with acute respiratory illness in children. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3655–64. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee WM, Kiesner C, Pappas T, Lee I, Grindle K, Jartti T, A diverse group of previously unrecognized human rhinoviruses are common causes of respiratory illnesses in infants. PLoS One. 2007;2:e966. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kistler A, Avila PC, Rouskin S, Wang D, Ward T, Yagi S, Pan-viral screening of respiratory tract infections in adults with and without asthma reveals unexpected human coronavirus and human rhinovirus diversity. J Infect Dis. 2007;196:817–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Renwick N, Schweiger B, Kapoor V, Liu Z, Villari J, Bullmann R, A recently identified rhinovirus genotype is associated with severe respiratory-tract infection in children in Germany. J Infect Dis. 2007;196:1754–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khetsuriani N, Kazerouni NN, Erdman DD, Lu X, Redd SC, Anderson LJ, Prevalence of viral respiratory tract infections in children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:314–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swofford DL. PAUP*: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimmony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2001.
- Andries K, Dewindt B, Snoeks J, Wouters L, Moereels H, Lewi PJ, Two groups of rhinoviruses revealed by a panel of antiviral compounds present sequence divergence and differential pathogenicity. J Virol. 1990;64:1117–23.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ledford RM, Collett MS, Pevear DC. Insights into the genetic basis for natural phenotypic resistance of human rhinoviruses to pleconaril. Antiviral Res. 2005;68:135–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Winther B, Hayden FG, Hendley JO. Picornavirus infections in children diagnosed by RT-PCR during longitudinal surveillance with weekly sampling: association with symptomatic illness and effect of season. J Med Virol. 2006;78:644–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jartti T, Lehtinen P, Vuorinen T, Koskenvuo M, Ruuskanen O. Persistence of rhinovirus and enterovirus RNA after acute respiratory illness in children. J Med Virol. 2004;72:695–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Part of the information in this article was presented at the International Conference of the American Thoracic Society, May 16–21, 2008, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
2Current affilation: California Department of Public Health, Richmond, California, USA.