Volume 14, Number 4—April 2008
Research
Emericella quadrilineata as Cause of Invasive Aspergillosis
Figure 1
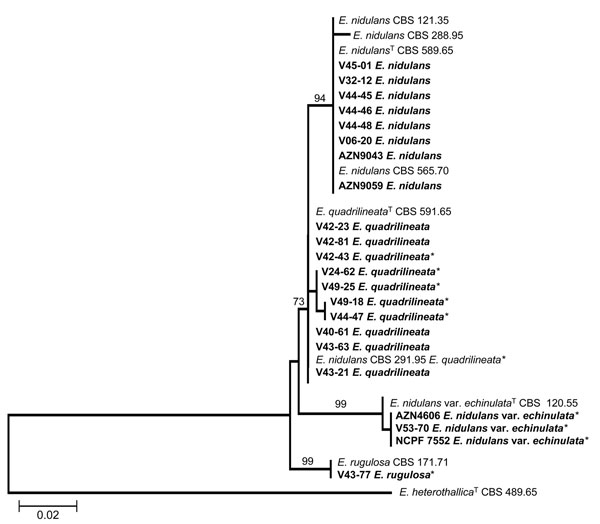
Figure 1. Neighbor-joining tree based on β-tubulin sequence data of the Emericella isolates examined. Clinical isolates are set in boldface. Numbers above branches are bootstrap values. Only values >70% are indicated. T indicates the type strain; * indicates the isolates that had been misidentified by morphologic identification as E. nidulans. Scale bar represents genetic distance calculated by the Kimura 2-parameter model (18).
References
- Pagano L, Caira M, Picardi M, Candoni A, Melillo L, Fianchi L, Invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia: update on morbidity and mortality—SEIFEM-C report. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:1524–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Joshi KR, Mathur DR, Sharma JC, Vyas MC, Sanghvi A. Mycetoma caused by Aspergillus nidulans in India. J Trop Med Hyg. 1985;88:41–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Knudtson WU, Kirkbride CA. Fungi associated with bovine abortion in the northern plains states (USA). J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992;4:181–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lucas GM, Tucker P, Merz WG. Primary cutaneous Aspergillus nidulans infection associated with a Hickman catheter in a patient with neutropenia. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1594–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dotis J, Roilides E. Osteomyelitis due to Aspergillus spp. in patients with chronic granulomatous disease: comparison of Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Int J Infect Dis. 2004;8:103–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Winkelstein JA, Marino MC, Johnston RB Jr, Boyle J, Curnutte J, Gallin JI, Chronic granulomatous disease. Report on a national registry of 368 patients. Medicine. 2000;79:155–69. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Van ‘t Hek LG, Verweij PE, Weemaes CM, Van Dalen R, Yntema JB, Meis JF. Successful treatment with voriconazole of invasive aspergillosis in chronic granulomatous disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1694–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Berger PE, Warris A, Weemaes CM. Preventing fungal infections in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1190–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dotis J, Panagopoulou P, Filioti J, Winn R, Toptsis C, Panteliadis C, Femoral osteomyelitis due to Aspergillus nidulans in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease. Infection. 2003;31:121–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Morris A, Schell WA, McDonagh D, Chaffee S, Perfect JR. Pneumonia due to Fonsecaea pedrosoi and cerebral abscesses due to Emericella nidulans in a bone marrow transplant recipient. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;21:1346–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gugnani HC, Vijayan KK, Tyagi P, Sharma S, Stchigel AM, Guarro J. Onychomycosis due to Emericella quadrilineata. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:914–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Henry T, Iwen PC, Hinrichs SH. Identification of Aspergillus species using internal transcribed spacer regions 1 and 2. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1510–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Glass NL, Donaldson GC. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995;61:1323–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Samson RA, Houbraken JAMP, Kuijpers AFA, Frank JM, Frisvad JC. New ochratoxin or sclerotium producing species in Aspergillus section Nigri. Stud Mycol. 2004;50:45–61.
- Hong SB, Cho HS, Shin HD, Frisvad JC, Samson RA. Novel Neosartorya species isolated from soil in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006;56:477–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG. The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:4876–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980;16:111–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Felsenstein J. PHYLIP (Phylogeny inference package), version 3.57c. Seattle: University of Washington; 1995.
- Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4:406–25.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution Int J Org Evolution. 1985;39:783–91. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Swofford T. PAUP*: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, version 4.0. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi. Approved standard M38-A. Wayne (PA): The Committee; 2002.
- Kurtz MB, Heath IB, Marrinan J, Dreikorn S, Onishi J, Douglas C. Morphological effects of lipopeptides against Aspergillus fumigatus correlate with activities against (1,3)-D-glucan synthase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994;38:1480–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Horie Y. Ascospore ornamentation and its application to the taxonomic re-evaluation in Emericella [in Japanese]. Transactions of the Mycological Society of Japan. 1980;21:483–93.
- Polacheck I, Nagler A, Okon E, Drakos P, Plaskowitz J, Kwon-Chung KJ. Aspergillus quadrilineatus, a new causative agent of fungal sinusitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:3290–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drakos PE, Nagler A, Or R, Naparstek E, Kapelushnik J, Engelhard D, Invasive fungal sinusitis in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1993;12:203–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ng KP, Saw TL, Madasamy M, Soo Hoo T. Onychomycosis in Malaysia. Mycopathologia. 1999;147:29–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tong QJ, Chai WX, Wang ZF, Kou JF, Qi ZT, Wang DL. A case of cerebral aspergillosis caused by Aspergillus nidulans. Clinical, pathologic and mycologic identifications. Chin Med J (Engl). 1990;103:518–22.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yano S, Kobayashi K, Shishido S, Nakano H. Intrabronchial Aspergillus nidulans infection in an immunocompetent man. Intern Med. 1999;38:372–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh MP, Singh CM. Fungi associated with suppurative mycosis of cattle and sheep in India. Indian J Anim Health. 1970;9:432–49.
- White CJ, Kwon-Chung KJ, Gallin JI. Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. An unusual case of infection with Aspergillus nidulans var. echinulatus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988;90:312–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mitchell RG, Chaplin AJ, Mackenzie DW. Emericella nidulans in a maxillary sinus fungal mass. J Med Vet Mycol. 1987;25:339–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Balajee SA, Gribskov J, Brandt M, Ito J, Fothergill A, Marr KA. Mistaken identity: Neosartorya pseudofischeri and its anamorph masquerading as Aspergillus fumigatus. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:5996–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Balajee SA, Nickle D, Varga J, Marr KA. Molecular studies reveal frequent misidentification of Aspergillus fumigatus by morphotyping. Eukaryot Cell. 2006;5:1705–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE, May GS, Osherov N, Rinaldi MG. Aspergillus nidulans is frequently resistant to amphotericin B. Mycoses. 2002;45:406–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh J, Rimek D, Kappe R. Intrinsic in vitro susceptibility of primary clinical isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus terreus, Aspergillus nidulans, Candida albicans and Candida lusitaniae against amphotericin B. Mycoses. 2006;49:96–103. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bowman JC, Abruzzo GK, Flattery AM, Gill CJ, Hickey EJ, Hsu MJ, Efficacy of caspofungin against Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus terreus, and Aspergillus nidulans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:4202–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: July 14, 2010
Page updated: July 14, 2010
Page reviewed: July 14, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.