Volume 15, Number 10—October 2009
Research
A Model-based Assessment of Oseltamivir Prophylaxis Strategies to Prevent Influenza in Nursing Homes
Figure 1
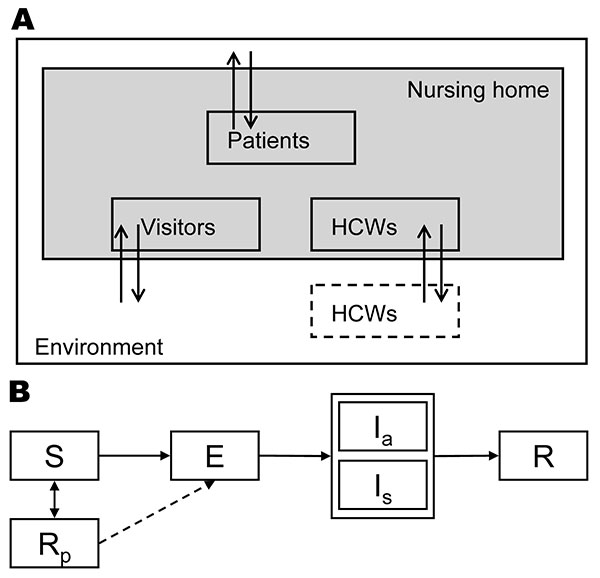
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of our stochastic individual-based model. A) The different types of persons in the nursing home: patients, healthcare workers (HCWs), and visitors. B) The time course of infection: S, susceptible; E, exposed; Ia, infectious and asymptomatic; Is, infectious and symptomatic; R, recovered/immune; Rp, immune while using prophylaxis. For all patients and HCWs in the model, we kept track of their stage in this infection cycle in time. If the influenza strain that is transmitted is resistant to oseltamivir, persons in the Rp department can still become infected (dashed arrow).
Page created: December 07, 2010
Page updated: December 07, 2010
Page reviewed: December 07, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.