Volume 16, Number 6—June 2010
Dispatch
Novel Norovirus in Dogs with Diarrhea
Figure
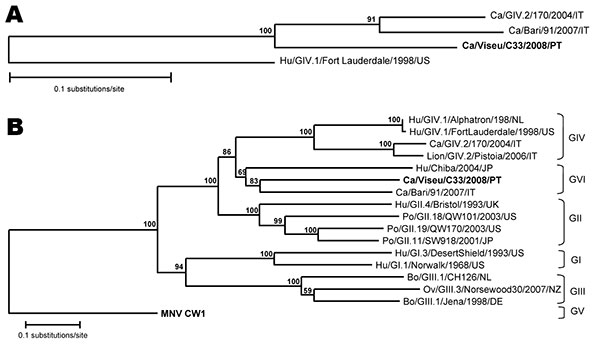
Figure. Phylogenetic trees of A) a 206-nt region of the RNA-dependent polymerase gene of 1 human genogroup (G) IV strain (Hu/GIV.1/FortLauderdale/1998/US), 2 recently published canine noroviruses (GIV.2/170/2004/IT, Bari/91/2007/IT) (5,13), and the novel canine Viseu strain reported in the study (boldface); and B) full-length amino acid sequence of viral protein (VP) 1 of norovirus strains of GI–GV detected in animals and human strains Hu/GI.1/Norwalk/1968/US, Hu/GI.3/DesertShield/1993/US, and Hu/GII.4/Bristol/1993/UK. The Viseu strain (boldface) forms tentatively a novel genogroup (GVI) with strains Ca/Bari/91/2007/IT and Hu/Chiba/2004/JP. Phylogenetic analysis was performed by using TreeCon software with Jukes and Cantor correction with bootstrap analysis (n = 1,000), and the tree topology was inferred by using neighbor-joining. Ca, canine; Hu, human; Po, porcine; Bo, bovine; Ov, ovine; Mu, murine.
References
- Glass RI, Parashar UD, Estes MK. Norovirus gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1776–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Patel MM, Hall AJ, Vinjé J, Parashar UD. Noroviruses: a comprehensive review. J Clin Virol. 2009;44:1–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van der Poel WH, Vinjé J, van der Heide R, Herrera MI, Vivo A, Koopmans MP. Norwalk-like calicivirus genes in farm animals. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6:36–41.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mattison K, Shukla A, Cook A, Pollari F, Friendship R, Kelton D, Human noroviruses in swine and cattle. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1184–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martella V, Lorusso E, Decaro N, Elia G, Radogna A, D’Abramo M, Detection and molecular characterization of a canine norovirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1306–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Farkas T, Sestak K, Wei C, Jiang X. Characterization of a rhesus monkey calicivirus representing a new genus of Caliciviridae. J Virol. 2008;82:5408–16. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martella V, Campolo M, Lorusso E, Cavicchio P, Camero M, Bellacicco A, Norovirus in captive lion cub (Panthera leo). Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1071–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jiang X, Huang PW, Zhong WM, Farkas T, Cubitt DW, Matson DO. Design and evaluation of a primer pair that detects both Norwalk- and Sapporo-like caliciviruses by RT-PCR. J Virol Methods. 1999;83:145–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vennema H, Bruin E, Koopmans M. Rational optimization of generic primers used for Norwalk-like virus detection by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Virol. 2002;25:233–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vinjé J, Koopmans MPG. Simultaneous detection and genotyping of “Norwalk-like viruses” by oligonucleotide array in a reverse line blot hybridization format. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:2595–601.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pratelli A, Tempesta M, Greco G, Martella V, Buonavoglia C. Development of a nested PCR assay for the detection of canine coronavirus. J Virol Methods. 1999;80:11–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pereira CA, Monezi TA, Mehnert DU, D’Angelo M, Durigon EL. Molecular characterization of canine parvovirus in Brazil by polymerase chain reaction assay. Vet Microbiol. 2000;75:127–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martella V, Decaro N, Lorusso E, Radogna A, Moschidou P, Amorisco F. Genetic heterogeneity and recombination in canine noroviruses. J Virol. 2009;83:11391–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Widdowson MA, Rockx B, Schepp R, van der Poel WH, Vinje J, van Duynhoven YT, Detection of serum antibodies to bovine norovirus in veterinarians and the general population in the Netherlands. J Med Virol. 2005;76:119–28. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grøndalen J, Sævik B, Sørum H. Companion animals as reservoir for zoonotic diseases. European Journal of Companion Animal Practice. 2008;18:213–22.