Volume 16, Number 8—August 2010
Perspective
Hantavirus Infections in Humans and Animals, China
Figure 4
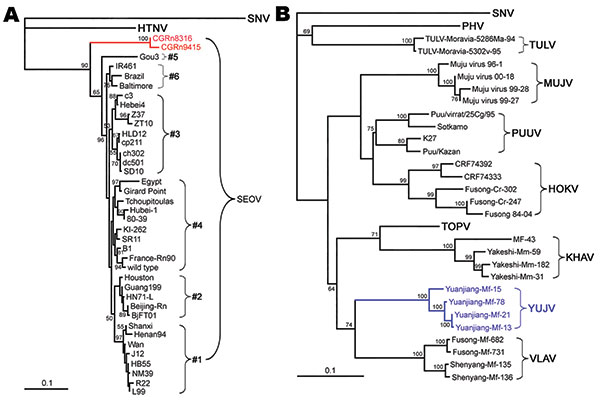
Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of Seoul virus (SEOV) variants according to partial (nt 2001–2301) medium segment sequences (A). Phylogenetic tree of hantaviruses according to complete coding sequences of the medium segment (B). PHYLIP program package version 3.65 (http://helix.nih.gov/Applications/phylip.html) was used to construct the phylogenetic trees; the neighbor-joining method was used. Bootstrap values were calculated from 1,000 replicates; only values >50% are shown at the branch nodes. The trees constructed by using the maximum-likelihood method (not shown) had similar topology. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site. Colors (blue and red) highlight viruses of interest from China. SNV, Sin Nombre virus; HTNV, Hantaan virus; PHV, Prospect Hill virus; SEOV, Seoul virus; TULV, Tula virus; MUJV, Muju virus; PUUV, Puumala virus; HOKV, Hokkaido virus; KHAV, Khabarovsk virus; YUJV, Yuanjiang virus; VLAV, Vladivostok virus.