Volume 5, Number 1—February 1999
Dispatch
Mycoplasma penetrans Bacteremia and Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome1
Figure 2
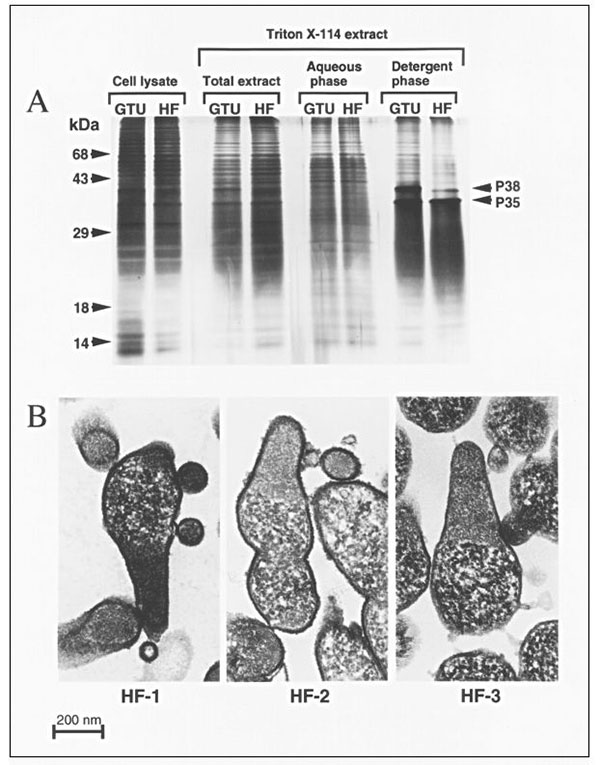
Figure 2. HF isolates belong to the species Mycoplasma penetrans. A. Comparison of protein patterns from the type strain of M. penetrans and the isolate HF-1. Mycoplasma cells were directly lysed with SDS (cell lysate), or antigens were extracted with the neutral detergent Triton X-114 (total extract). Antigens were further separated after partitioning between the aqueous and detergent phases. The two mycoplasmas compared are the M. penetrans type strain GTU-54-6A1 (GTU) and the isolate HF. B. Ultrastructural features of the M. penetrans isolates HF-1, HF-2 and HF-3. The HF isolates were passaged four times in SP-4 broth without antibiotics and processed for transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Ultrathin sections were stained with osmiun tetroxide and ruthenium red and observed by TEM. The three isolates show the typical elongated, flask-shaped morphology of M. penetrans, with the two divided internal compartments. The cytoplasm is limited by a single triple-layered unit membrane that is covered with capsular material.
1Presented in part at the 11th International Congress of the International Organization for Mycoplasmology. July 14–19, 1996. Orlando, FL, USA.