Volume 5, Number 1—February 1999
Research
Dual and Recombinant Infections: An Integral Part of the HIV-1 Epidemic in Brazil
Figure 1
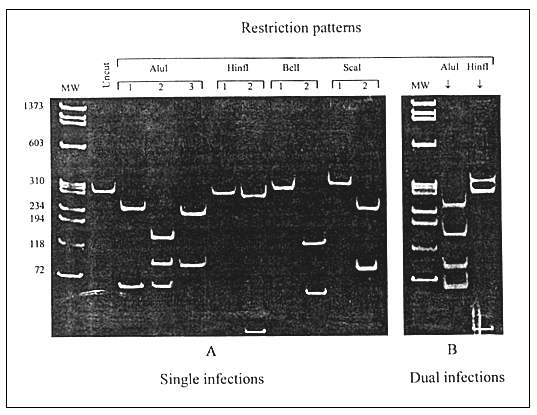
Figure 1. Differentiation between single (A) and dual (B) HIV-1 infections by the restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the polymerase chain reaction—amplified prt. A: Three AluI digestion patterns represent subtypes A, C, and F (pattern 1) and subtypes B and D (patterns 2 and 3); two HinfI patterns represent subtypes D (pattern 1) and B (pattern 2); two BclI patterns represent subtypes F (patterns 1) and A and C (pattern 2); two ScaI patterns represent subtypes A (pattern 1) and C (pattern 2). B: Two AluI digestion patterns (1 and 2) in the dually infected patient with HIV-1 subtypes F and B; two HinfI patterns (1 and 2) in the patient infected with subtypes B and D viruses.
References
- Leitner T. Genetic subtypes of HIV-1. In: Myers G, Foley B, Mellors JW, Korber B, Jeang KT, Wain-Hobson S, editors. Human Retroviruses and AIDS. Theoretical Biology and Biophysics, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico; 1996: III28-40.
- Hu DJ, Dondero TJ, Rayfield MA, George JR, Schochetman G, Jaffe HW, The emerging genetic diversity of HIV. The importance of global surveillance for diagnostics, research, and prevention. JAMA. 1996;275:210–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Robertson DL, Sharp PM, McCutchan FE, Hahn BH. Recombination in HIV-1. Nature. 1995;374:124–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Artenstein AW, VanCott TC, Mascola JR, Carr JC, Hegerich PA, Gaywee J, Dual infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 of distinct envelope subtypes in humans. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:805–10.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pieniazek D, Janini LM, Ramos A, Tanuri A, Schechter M, Peralta JM, HIV-1 patients may harbor viruses of different phylogenetic subtypes: implications for the evolution of the HIV/AIDS pandemic. Emerg Infect Dis. 1995;1:86–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Janini LM, Tanuri A, Schechter M, Peralta JM, Vicente AC, Dela Torre N, Horizontal and vertical transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 dual infections caused by viruses of subtypes B and C. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:227–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Janini LM, Pieniazek D, Peralta JM, Schechter M, Tanuri A, Vicente AC, Identification of single and dual infections with distinct subtypes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by using restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Virus Genes. 1996;13:69–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moran N, Soler A, Flores I, Alegria M, Vera M, Pieniazek D, Multi-strain HIV-1 infection among female sex workers in Puerto Rico: emerging pattern of HIV-1 epidemic. 4th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections [abstract 170]. Washington DC, January 1997.
- Kampinga G, Simonon A, van de Perre P, Karita E, Maellati P, Goudsmit J. Primary infections with HIV of women and their offspring in Rwanda: Findings of heterogeneity at seroconversion, coinfection and recombinants of HIV-1 subtypes A and C. Virology. 1997;227:63–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Takehisa J, Zekeng L, Mlura T, Ido E, Yamashita M, Mboudjeka I, Triple HIV-1 infection with group O and group M of different clades in a single Cameroonian AIDS patient. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1997;14:81–2.
- Pieniazek D, Janini ML, Ramos A, Bandea C, Soriano V, Downing R, Mixed infections with HIV-1 strains of different phylogenetic subtypes: implication for the evolution of the HIV/AIDS pandemic. 3rd Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections [abstract]. Washington DC, January 1996.
- Carr JK, Salminen MO, Koch D, Gotte A, Artenstein AW, Hegerich PA. at al. Full length sequence and mosaic structure of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate from Thailand. J Virol. 1996;70:5935–43.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wasi C, Herring B, Raktham S, Vanichseni S, Mastro TD, Young NL, Determination of HIV-1 subtypes in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand, using peptide-binding enzyme immunoassay and heteroduplex mobility assay: evidence of increasing infection with HIV-1 subtype E. AIDS. 1995;9:843–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abimicu AG, Stern TL, Zwandor A. Subgroup G HIV-type 1 isolates from Nigeria. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994;10:1581–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brazilian Ministry of Health. Boletim Epidemiologico-AIDS: Semana Epidemiologica-36 a 48-setembro a novembro de 1997. 1997;10:no 04 [http//www.aids.gov.br].
- Potts KE, Kalish ML, Lott T, Orloff G, Luo CC, Bernard MA, Genetic heterogeneity of the V3 region of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein in Brazil. AIDS. 1993;7:1191–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pinto ME, Tanuri A, Schechter M. Molecular and epidemiologic evidence for the discontinuous introduction of subtypes B and F into Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1998. In press.
- Louwagie J, Delwart EL, Mullins JI, McCutchan FE, Eddy G, Burke DS, Genetic analysis of HIV-1 isolates from Brazil reveals presence of two distinct genetic subtypes. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994;10:561–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Morgado MG, Sabino EC, Shpaer EG, Bongertz V, Brigido L, Guimaraes MD, V3 region polymorphisms in HIV-1 from Brazil: prevalence of subtype B strains divergent from North American/European prototype and detection of subtype F. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994;10:569–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. HIV type 1 variation in World Health Organization-sponsored vaccine evaluation sites: genetic screening, sequence analysis, and preliminary biological characterization of selected viral strains. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994;10:1327–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sabino EC, Diaz RS, Brigido LF, Learn GH, Mullins JI, Reingold AL, Distribution of HIV-1 subtypes seen in an AIDS clinic in Sao Paulo City, Brazil. AIDS. 1996;10:1579–84.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sabino EC, Shpaer EG, Morgado MG, Korber BT, Diaz RS, Bongertz V, Identification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope genes recombinant between subtypes B and F in two epidemiologically linked individuals from Brazil. J Virol. 1994;68:6340–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schechter M, Zajdenverg R, Machado LL, Pinto ME, Lima LA, Perez MA. Predicting CD4 counts in HIV-infected Brazilian individuals: a model based on the World Health Organization staging system. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1994;7:163–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhu T, Wang N, Carr A, Wolinsky S, Ho D. Evidence for coinfection by multiple strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype B in an acute seroconvertor. J Virol. 1995;69:1324–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Delwart EL, Shpaer EG, Louwagie J, McCutchan FE, Grez M, Rubsamen-Waigmann H, Genetic relationships determined by a DNA heteroduplex mobility assay: analysis of HIV-1 env genes. Science. 1993;262:1257–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ou CY, Ciesielski CA, Myers G, Bandea CI, Luo CC, Korber BT, Molecular epidemiology of HIV transmission in a dental practice. Science. 1992;256:1165–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Higgins DG, Sharp PM. Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989;5:151–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maidak BL, Larsen N, McCaughey MJ, Overbeek R, Olsen GJ, Fogel K, The Ribosomal Database Project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:3485–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Felsenstein J. PHYLIP-phylogeny interference package (version 3.2). Cladistics. 1989;5:164–6.
- Meyerhans A, Vartanian JP, Wain-Hobson S. DNA recombination during PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18:1687–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Simmonds P, Balfe P, Peutherer JF, Ludlam CA, Bishop JO, Brown AJ. Human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals contain provirus in small numbers of peripheral mononuclear cells and at low copy numbers. J Virol. 1990;64:864–72.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): interim proposal for a WHO staging system for HIV infection and disease. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 1990;65:221–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cornelissen M, Kampinga G, Zorgdrager F, Goudsmit J; UNAIDS Network for HIV Isolation and Characterization. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes defined by env show high frequency of recombinant gag genes. J Virol. 1996;70:8209–12.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tanuri A, Swanson P, Devare S, Berro OJ, Savedra A, Costa LJ, HIV-1 subtypes among blood donors from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1998. In press.
Page created: December 10, 2010
Page updated: December 10, 2010
Page reviewed: December 10, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.