Volume 6, Number 1—February 2000
Dispatch
Molecular Genetic Evidence of a Novel Morbillivirus in a Long-Finned Pilot Whale (Globicephalus melas)
Figure 2
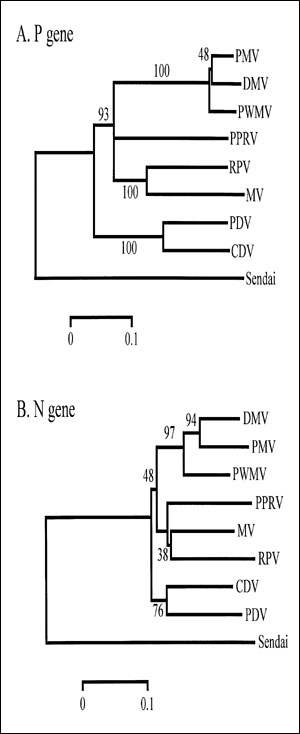
Figure 2. Neighbor-joining analyses of partial P and N gene sequences with branch distances as shown. Analyses were performed with MEGA, version 1.01 (13). For the P gene, a 378 nucleotide fragment was amplified (7,8) using the following primers: 5'-CGGAG ACCGAGTCTTCATT-3' (forward) and 5'-ATTGGGTTGC ACCACTTG TC-3' (reverse), corresponding to nucleotides 2190 to 2567 as aligned to the measles virus P gene (Edmonston strain). For the N gene, a 230-nucleotide fragment was amplified using the following primers: 5'-CCHAGRATYGCTGAAATGATHTGTGA-3' (forward) and 5'-AACTTG TTCTGRATWGAGTTYTC-3' (reverse), corresponding to nucleotides 849 to 1078, as aligned to the measles virus N gene (Edmonston strain, GenBank accession number Z66517). RT-PCR and sequence analysis were performed as described (7,8).
References
- Kennedy S. Morbillivirus infections in aquatic mammals. J Comp Pathol. 1998;119:201–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lipscomb TP, Schulman FY, Moffett D, Kennedy S. Morbilliviral disease in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from the 1987-1988 epizootic. J Wildl Dis. 1994;30:567–71.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schulman FY, Lipscomb TP, Moffett D, Krafft AE, Lichy JH, Tsai MM, Reevaluation of the 1987-88 Atlantic coast bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) mortality event with histologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular evidence for a morbilliviral etiology. Vet Pathol. 1997;34:288–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Osterhaus ADME, Groen J, Spijkers HEM, Broeders HWJ, UytdeHaag FGCM, de Vries P, . Mass mortality in seals caused by a newly discovered morbillivirus. Vet Microbiol. 1990;23:343–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kennedy S, Smyth JA, Cush PF, McAliskey M, McCullough SJ, Rima BK. Seven histopathologic and immunocytochemical studies of distemper in harbor porpoises. Vet Pathol. 1991;28:1–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Domingo M, Vilafranca M, Visa J, Prats N, Trudgett AL, Visser I. Evidence of chronic morbillivirus infection in the Mediterranean striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba). Vet Microbiol. 1995;44:229–39. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Krafft AE, Lichy JH, Lipscomb TP, Klaunberg BA, Kennedy S, Taubenberger JK. Postmortem diagnosis of morbillivirus infection in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico epizootics by a polymerase chain reaction-based assay. J Wildl Dis. 1995;31:410–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lipscomb TP, Kennedy S, Moffett D, Krafft AE, Klaunberg BA, Lichy JH, Morbilliviral epizootic in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins of the Gulf of Mexico. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1996;8:283–90.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reidarson TH, McBain J, House C, King DP, Stott JL, Krafft AE, Morbillivirus infection in stranded common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) from the Pacific Ocean. J Wildl Dis. 1998;34:771–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barrett T, Visser IKG, Mamaev L, Goatley L, van Bressem M-F, Osterhaus ADME. Dolphin and porpoise morbilliviruses are genetically distinct from phocine distemper virus. Virology. 1993;193:1010–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taubenberger JK, Tsai MM, Krafft AE, Lichy JH, Reid AH, Schulman FY, Two different morbilliviruses implicated in bottlenose dolphin epizootics. Emerg Infect Dis. 1996;2:213–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swofford DL. PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony, version 3.1.1 (Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, Illinois; 1991.
- Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis, version 1.01. Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania; 1993.
- Duignan PJ, House C, Geraci JR, Duffy N, Rima BK, Walsh MT, Morbillivirus infection in cetaceans of the western Atlantic. Vet Microbiol. 1995;44:241–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Duignan PJ, House C, Geraci JR, Early G, Copland HG, Walsh MT, Morbillivirus infection in two species of pilot whales (Globicephala sp.) from the western Atlantic. Mar Mamm Sci. 1995;11:150–62. DOIGoogle Scholar