Volume 10, Number 4—April 2004
Research
Antigenic and Genetic Variability of Human Metapneumoviruses
Figure 1
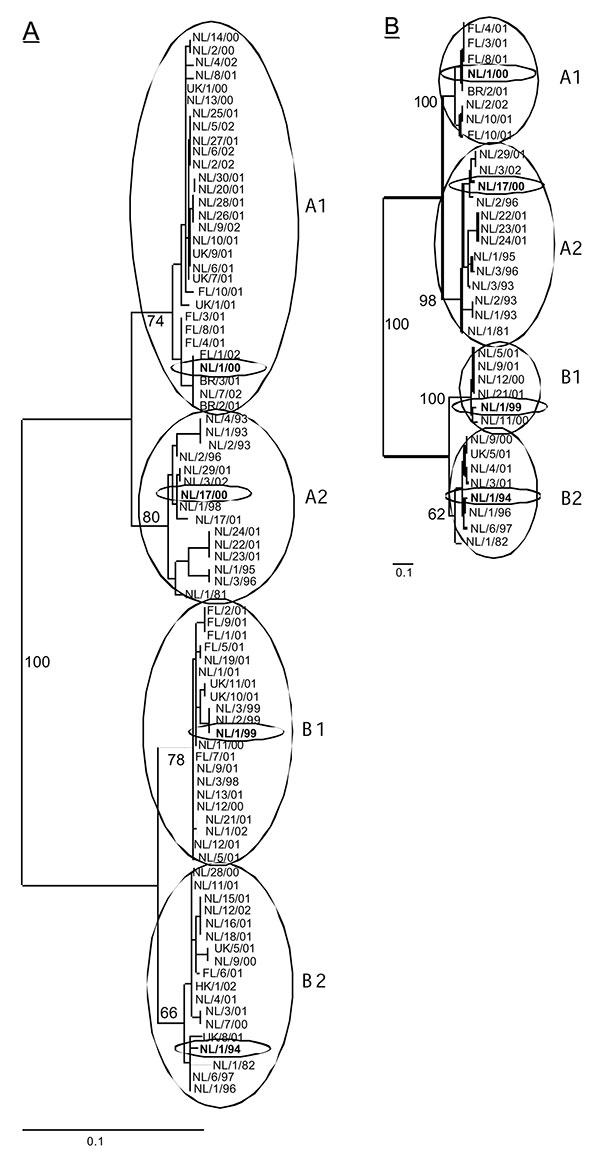
Figure 1. Phylogenetic trees constructed based on the (A) partial F gene (ORF position 780–1,221, n = 84) or (B) the complete G coding region (start G ORF to start L ORF, n = 35). Trees were generated by maximum likelihood analysis using 100 bootstraps and 3 jumbles. The scale representing the percentage of nucleotide changes is shown for each tree. Bootstrap values are based on the consensus trees, and relevant numbers are shown in the tree. The four prototype viruses are shown in boldface, with ovals drawn around them. NL, viruses from the Netherlands; FN, viruses obtained from Finland; UK, viruses obtained from the United Kingdom; HK, viruses obtained from Hong Kong; BR, viruses obtained from Brazil.
Page created: February 09, 2011
Page updated: February 09, 2011
Page reviewed: February 09, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.