Volume 10, Number 4—April 2004
Research
Antigenic and Genetic Variability of Human Metapneumoviruses
Figure 3
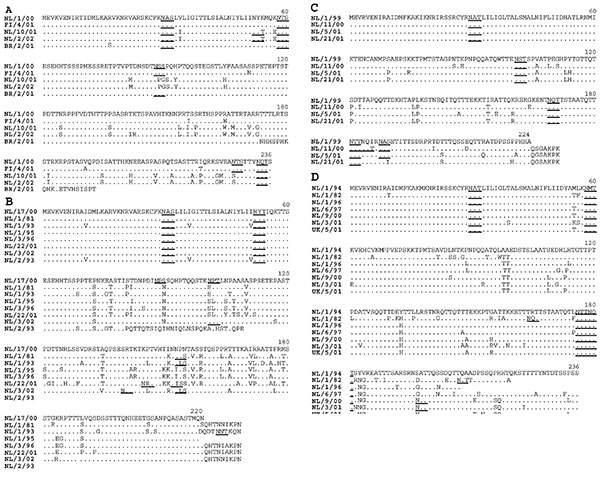
Figure 3. Amino acid sequence comparison of the putative attachment (G) protein of human metapneumovirus strains per genetic sublineage. For each sublineage only representative samples are depicted, resulting in 24 sequences. Representative sequences were chosen, so that from each year in which samples were obtained at least one sequence is depicted, and sequences with only a few amino acid substitutions were omitted. Potential N-linked glysosylation sites are underlined, and periods indicate the position of identical amino acid residues relative to the first sequence in each subgroup. Numbers indicate the nucleotide position in the primary G ORF.
Page created: February 09, 2011
Page updated: February 09, 2011
Page reviewed: February 09, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.