Volume 11, Number 8—August 2005
Research
Optimizing Treatment of Antimicrobial-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Figure 3
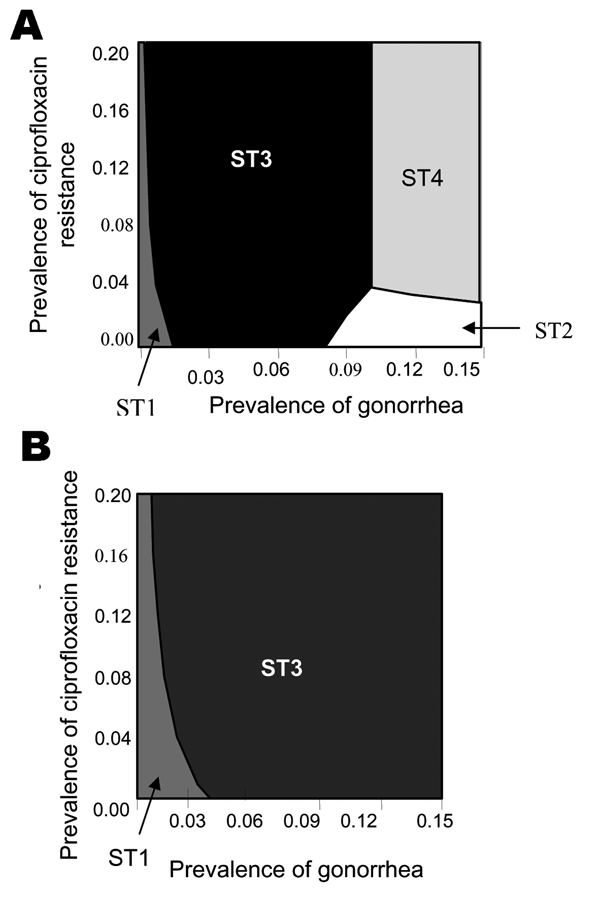
Figure 3. . Lowest cost per patient successfully treated on varying sensitivity and specificity of culture- and nonculture-based tests. A) Culture: sensitivity = 75%, specificity = 95%; nonculture: sensitivity = 85%, specificity = 95%. For notes, see Figure 1 legend. B) Culture: sensitivity = 95%, specificity = 97%; nonculture: sensitivity = 85%, specificity = 95%.
1In 2000, only 18% of gonorrhea tests performed by public health laboratories in the United States were culture-based tests.
2Monte Carlo simulation involves specifying a probability distribution of values for model inputs. A computer algorithm then runs the model for several iterations. During each iteration, the computer algorithm selects input values from the probability distributions, and calculates the output (e.g., cost per patient successfully treated). After the final run, the model provides results such as the mean, median, and 5th and 95th percentiles for each specified output.