Volume 11, Number 9—September 2005
Research
Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-associated Coronavirus, Beijing
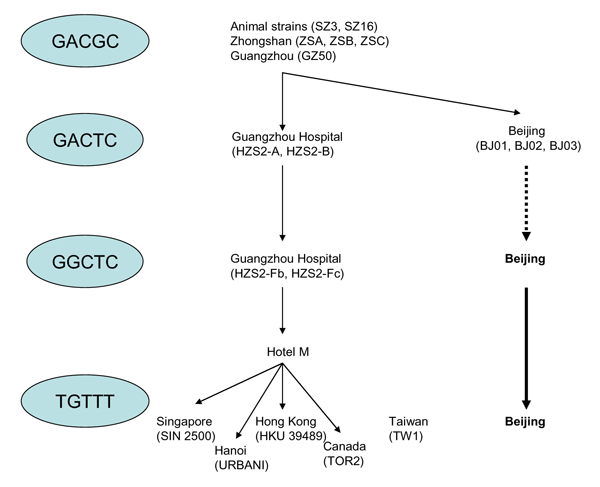
Figure
References
- World Health Organization. SARS epidemiology to date [monograph on the Internet]. 2003. [cited 2003 Apr 11]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/sars/epi2003_04_11/en/
- World Health Organization. Multicentre Collaborative Network for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Diagnosis. A multicentre collaboration to investigate the cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2003;361:1730–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Cumulative number of reported probable cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) [monograph on the Internet]. [cited 2003 Jul 11]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/en/
- Guan Y, Peiris JS, Zheng B, Poon LL, Chan KH, Zeng FY, Molecular epidemiology of the novel coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2004;363:99–104. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pang X, Zhu Z, Xu F, Guo J, Gong X, Liu D, Evaluation of control measures implemented in the severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak in Beijing, 2003. JAMA. 2003;290:3215–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rota PA, Oberste MS, Monroe SS, Nix WA, Campagnoli R, Icenogle JP, Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science. 2003;300:1394–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Marra MA, Jones SJ, Astell CR, Holt RA, Brooks-Wilson A, Butterfield YS, The genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science. 2003;300:1399–404. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chinese SARS Molecular Epidemiology Consortium. Molecular evolution of the SARS coronavirus during the course of the SARS epidemic in China. Science. 2004;303:1666–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhong NS, Zheng BJ, Li YM, Poon LLM, Xie ZH, Chan KH, Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People's Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet. 2003;362:1353–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ruan YJ, Wei CL, Ee AL, Vega VB, Thoreau H, Su ST, Comparative full-length genome sequence analysis of 14 SARS coronavirus isolates and common mutations associated with putative origins of infection. Lancet. 2003;361:1779–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tsui SK, Chim SS, Lo YM; Chinese University of Hong Kong Molecular SARS Research Group. Coronavirus genomic-sequence variations and the epidemiology of the severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:187–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Case definitions for surveillance of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). [cited 2003 Apr 29]. Available at: http://www.who.int/csr/sars/casedefinition/en
- Xu DP, Zhang Z, Chu Fl, Li Y, Jin L, Zhang L, Genetic variation of SARS coronavirus in Beijing hospital. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:789–94.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yeh SH, Wang HY, Tsai CY, Kao CL, Yang JY, Liu HW, Characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus genomes in Taiwan: molecular epidemiology and genome evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:2542–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tsang KW, Ho PL, Ooi GC, Yee WK, Wang T, Chan-Yeung M, A cluster of cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1977–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang Z, Li L, Luo Y, Zhang J, Wang M, Cheng S, Molecular biological analysis of genotyping and phylogeny of severe acute respiratory syndrome associated coronavirus. Chin Med J (Engl). 2004;117:42–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: April 23, 2012
Page updated: April 23, 2012
Page reviewed: April 23, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.