Volume 12, Number 6—June 2006
Research
Human Streptococcus suis Outbreak, Sichuan, China
Figure 5
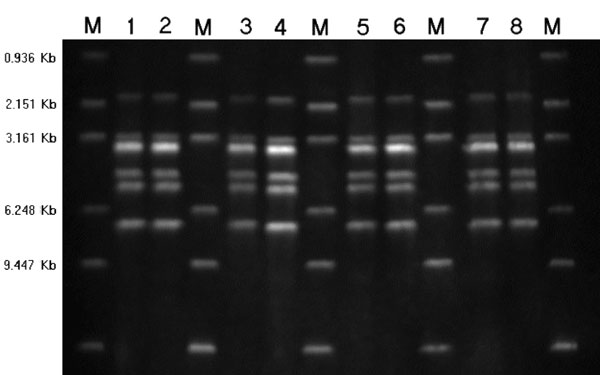
Figure 5. Ribotyping of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolates by PvuII restriction. Lane 1, deceased pig isolate SC5; lane 2, deceased pig isolate SC16; lane 3, patient isolate SC154; lane 4, patient isolate SC160; lane 5, patient isolate SC175; lane 6, patient isolate SC179; lane 7, patient isolate SC204; lane 8, patient isolate SC206; M, molecular size standard.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Members of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention Streptococcus suis study group are Wenjun Zhong, Ling Meng, Yongjun Gao, Huamao Du, Changyu Ye, Zhigang Cui, Shouyin Zhang, and Dong Jin. Members of the Sichuan Center for Disease Control and Prevention Streptococcus suis study group are Li Liu, Heng Yuan, Bin Ouyang, Qiang Lv, Yan Huang, Ting Huang, Xingyu Zhou, Liao Feng, and Qidi Pang.