Volume 13, Number 6—June 2007
Research
Molecular Characteristics and Epidemiology of Meningococcal Carriage, Burkina Faso, 2003
Figure 2
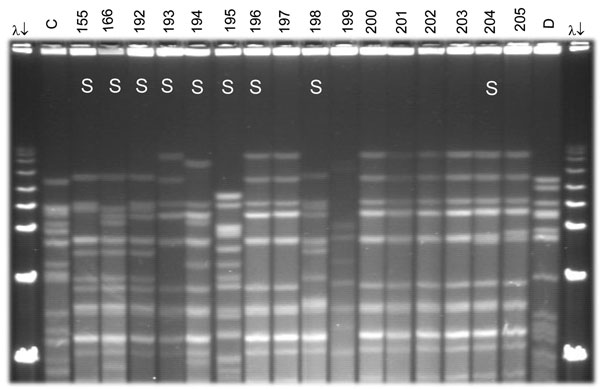
Figure 2. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) analysis of chromosomal DNA from pharyngeal meningococcus isolates (stained with ethidium bromide). Whole chromosome DNA macrorestriction fragments were generated by digestion with endonuclease SpeI. Shown are examples of sequence type (ST) prediction by PFGE in carried meningococci and diversity among STs types. S, isolates tested by multilocus sequence typing (MLST). Lanes λ (arrows) PFGE marker I (Boehringer Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany); lane C, ST-2881, meningitis case isolate, Niger 2003; lanes 155, 166, and 192–194, ST-192, NG:NT:NST; lane 195, ST-198, NG:15:P1.6; lanes 196–198, ST-192, NG:NT:NST; lane 199, isolate unrelated to the presented study; lanes 200–205, ST-192, NG:NT:NST; lane D, meningitis case isolate, ST-11, Niger 2003. Isolates 192, 193, 194, 196, 198, and 204 were identified as ST-192 by MLST. Isolates 197, 200, 201, 202, and 203 are indistinguishable from isolate 196 and are thus considered ST-192. ST-192 isolates from this study had 10 different PFGE patterns, of which 6 are represented by isolates 155, 166, 192, 194, 196, and 204.