Volume 14, Number 12—December 2008
Research
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus (H5N1) Infection in Red Foxes Fed Infected Bird Carcasses
Figure 1
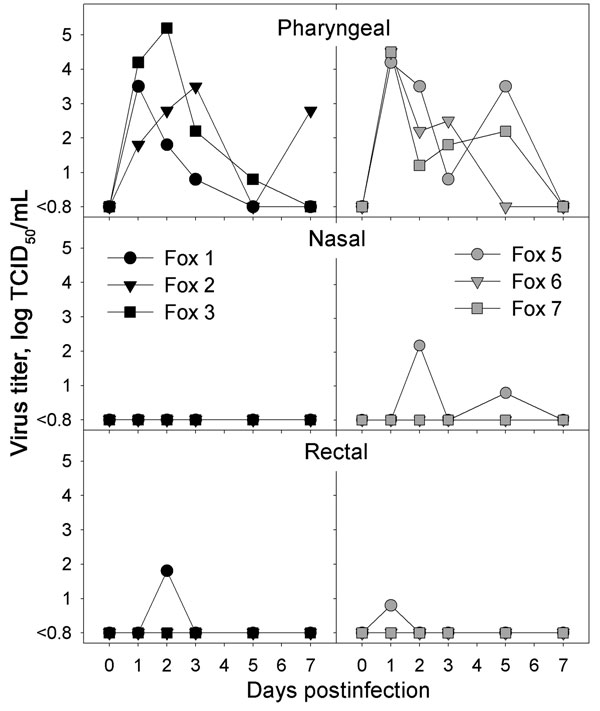
Figure 1. Infectious virus titers obtained from pharyngeal, nasal, and rectal swabs of foxes infected intratracheally with highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus (H5N1) (left, black symbols) or fed chicks infected with HPAI virus (H5N1) (right, gray symbols) at various time points after infection. No virus was isolated from any swabs of the negative-control foxes. TCID50, median tissue culture infectious dose.
Page created: July 22, 2010
Page updated: July 22, 2010
Page reviewed: July 22, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.