Volume 14, Number 2—February 2008
Research
Molecular Typing of Australian Scedosporium Isolates Showing Genetic Variability and Numerous S. aurantiacum
Figure 2
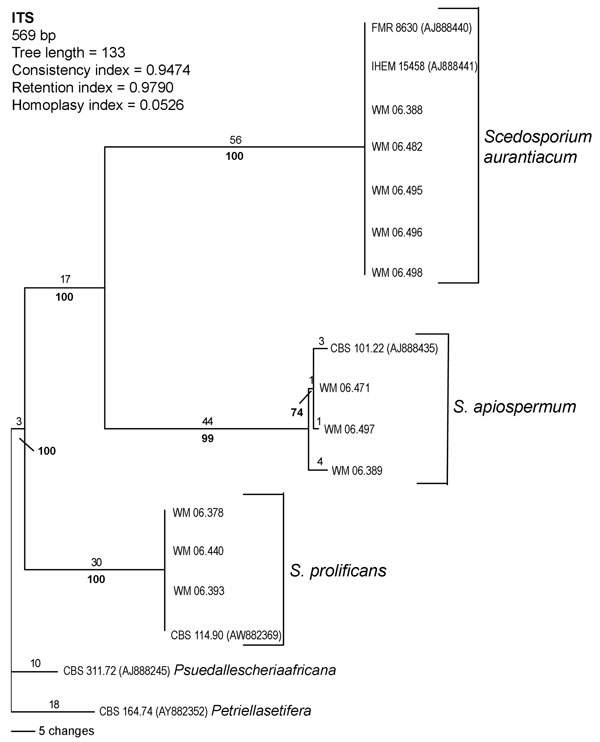
Figure 2. Rooted phylogram (outgroup Pseudallescheria africana CBS 311.72 and Petriella setifera CBS 164.74), showing the relationships among 11 selected strains representing each obtained internal transcribed spacer (ITS)–restriction fragment length polymorphism pattern and 4 reference strain sequences obtained from GenBank by using PAUP* version 4.06.10 (29).
References
- Rappuoli R. From Pasteur to genomics: progress and challenges in infectious diseases.Nat Med. 2004;10:1177–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nucci M. Emerging moulds: Fusarium, Scedosporium and Zygomycetes in transplant patients.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003;16:607–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Walsh TJ, Groll A, Hiemenez J, Fleming R, Roilides E, Anaissie E. Infections due to emerging and uncommon medically-important fungal pathogens.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10(Suppl 1):48–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Steinbach WJ, Perfect JR. Scedosporium species infections and treatments.J Chemother. 2003;15(Suppl 2):16–27.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gilgado F, Serena C, Cano J, Gene J, Guarro J. Antifungal susceptibilities of the species of the Pseudallescheria boydii complex.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:4211–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guarro J, Kantarcioglu AS, Horre R, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Cuenca Estrella M, Berenguer J, Scedosporium apiospermum: changing clinical spectrum of a therapy-refractory opportunist.Med Mycol. 2006;44:295–327. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Campagnaro EL, Woodside KJ, Early MG, Gugliuzza KK, Colome-Grimmer MI, Lopez FA, Disseminated Pseudallescheria boydii (Scedosporium apiospermum) infection in a renal transplant patient.Transpl Infect Dis. 2002;4:207–11.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williamson EC, Speers D, Arthur IH, Harnett G, Ryan G, Inglis TJ. Molecular epidemiology of Scedosporium apiospermum infection determined by PCR amplification of ribosomal intergenic spacer sequences in patients with chronic lung disease.J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:47–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cimon B, Carrere J, Vinatier JF, Chazalette JP, Chabasse D, Bouchara JP. Clinical significance of Scedosporium apiospermum in patients with cystic fibrosis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;19:53–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Defontaine A, Zouhair R, Cimon B, Carrere J, Bailly E, Symoens F, Genotyping study of Scedosporium apiospermum isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:2108–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gilgado F, Cano J, Gene J, Guarro J. Molecular phylogeny of the Pseudallescheria boydii species complex: proposal of two new species.J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4930–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wood GM, McCormack JG, Muir DB, Ellis DH, Ridley MF, Pritchard R, Clinical features of human infection with Scedosporium inflatum.Clin Infect Dis. 1992;14:1027–33.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Idigoras P, Perez-Trallero E, Pineiro L, Larruskain J, Lopez-Lopategui MC, Rodriguez N, Disseminated infection and colonization by Scedosporium prolificans: a review of 18 cases, 1990–1999.Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:e158–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Berenguer J, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Richard C, Alvarez M, Sanz M, Gaztelurrutia L, Deep infections caused by Scedosporium prolificans. A report on 16 cases in Spain and a review of the literature. Scedosporium prolificans Spanish Study Group.Medicine (Baltimore). 1997;76:256–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cooley L, Spelman D, Thursky K, Slavin M. Infection with Scedosporium apiospermum and S. prolificans, Australia.Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1170–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ruiz-Díez B, Martin-Diez F, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Alvarez M, Martinez-Suarez JV. Use of random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and PCR-fingerprinting for genotyping a Scedosporium prolificans (inflatum) outbreak in four leukemic patients.Curr Microbiol. 1997;35:186–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guerrero A, Torres P, Duran MT, Ruiz-Diez B, Rosales M, Rodriguez-Tudela JL. Airborne outbreak of nosocomial Scedosporium prolificans infection.Lancet. 2001;357:1267–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meyer W, Maszewska K, Amirmostofian M, Igreja RP, Hardtke C, Methling K, Molecular typing of global isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans by PCR-fingerprinting and RAPD—a pilot study to standardize techniques on which to base a detailed epidemiological survey.Electrophoresis. 1999;20:1790–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Solé M, Cano J, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Ponton J, Sutton DA, Perrie R, Molecular typing of clinical and environmental isolates of Scedosporium prolificans by inter-simple-sequence-repeat polymerase chain reaction.Med Mycol. 2003;41:293–300. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zouhair R, Defontaine A, Ollivier C, Cimon B, Symoens F, Hallet J-N, Typing of Scedosporium apiospermum by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and random amplification of polymorphic DNA.J Med Microbiol. 2001;50:925–32.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- San Millan R, Quindos G, Garaizar J, Salesa R, Guarro J, Ponton J. Characterization of Scedosporium prolificans clinical isolates by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis.J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:2270–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- International statistical classification of disease and related health problems, 10th revision, Australian Modification (ICD-10-AM). Sydney (Australia): National Centre for Classification in Health, University of Sydney; 1998.
- de Hoog GS, Guarro J, Gene J, Figuerras MJ. Hyphomycetes: Genus: Scedosporium. In: Atlas of clinical fungi. 2nd ed. Utrecht (the Netherlands): Centralbureau voor Schimmelcultures/Universitat Rovira i Virgili; 2000. p. 899–901.
- Ascioglu S, Rex JH, de Pauw B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F, Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoeitic stem cell transplants: an international consensus.Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:7–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vilgalys R, Hester M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species.J Bacteriol. 1990;172:4238–46.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Halliday CL, Carter DA. Clonal reproduction and limited dispersal in an environmental population of Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii isolates from Australia.J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:703–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swofford DL. PAUP* 4.06.10: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2003.
- Nei M, Li WH. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979;76:5269–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wetton JH, Carter RE, Parkin DT, Walters D. Demographic study of a wild house sparrow population by DNA fingerprinting.Nature. 1987;327:147–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rainer J, de Hoog GS, Wedde M, Graser Y, Gilges S. Molecular variability of Pseudallescheria boydii, a neurotropic opportunist.J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:3267–73.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Hoog GS, Marvin-Sikkema FD, Lahpoor GA, Gottschall JC, Prins RA, Gueho E. Ecology and physiology of Pseudallescheria boydii, an emerging opportunistic fungus.Mycoses. 1994;37:71–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gueho E, de Hoog GS. Taxonomy of the medical species of Pseudallescheria and Scedosporium.J Mycol Méd.1991;1:3–9.
- Rainer J, de Hoog GS. Molecular taxonomy and ecology of Pseudallescheria, Petriella and Scedosporium prolificans (Microascaceae) containing opportunistic agents on humans.Mycol Res. 2006;110:151–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bougnoux ME, Tavanti A, Bouchier C, Gow NA, Magnier A, Davidson AD, Collaborative consensus for optimized multilocus sequence typing of Candida albicans.J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:5265–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wedde M, Muller D, Tintelnot K, de Hoog GS, Stahl U. PCR-based identification of clinically relevant Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium strains.Med Mycol. 1998;36:61–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alvarez M, Lopez Ponga B, Rayon C, Garcia Gala J, Roson Porto MC, Gonzalez M, Nosocomial outbreak caused by Scedosporium prolificans (inflatum): four fatal cases in leukemic patients.J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:3290–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kidd SE, Hagen F, Tscharke RL, Huynh M, Bartlett KH, Fyfe M, A rare genotype of Cryptococcus gattii caused the cryptococcosis outbreak on Vancouver Island (British Columbia, Canada).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:17258–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tapia M, Richard C, Baro J, Salesa R, Figols J, Zurbano F, Scedosporium inflatum infection in immunocompromised hematological patients.Br J Haematol. 1994;87:212–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Idigoras P, Garcia-Arenzana JM, Saenz JR, Pineiro L, Marin J. Isolation of Scedosporium prolificans from the air in the room of a patient with leukemia and disseminated infection with this fungus.Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2000;18:426–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Salkin IF, McGinnis MR, Dykstra MJ, Rinaldi MG. Scedosporium inflatum, an emerging pathogen.J Clin Microbiol. 1988;26:498–503.PubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to experimental work and data analysis.
2Current affiilation: Lille Pasteur Institute, Lille, France
3Members of the Australian Scedosporium Study Group of the Australasian Society for Infectious Diseases: Australian Capital Territory: Peter Collignon; The Canberra Hospital. New South Wales: Richard Benn (Royal Prince Alfred Hospital); Ian Chambers (Douglass Hanly Moir Pathology); Sharon Chen (Westmead Hospital); Nelson Dennis (Wollongong Hospital); Deo DeWit (Gosford Hospital); John Ferguson (John Hunter Hospital); Iain Gosbell (Liverpool Hospital); Thomas Gottlieb (Concord Hospital); Catriona Halliday (Westmead Hospital); Juliette Holland (Mayne Laverty Pathology); Alison Kesson (New Children’s Hospital, Westmead); Richard Lawrence (St. George Hospital); Deborah Marriott (St. Vincent’s Hospital, Sydney); Wieland Meyer (Westmead Hospital); Peter Newton (Wollongong Hospital); Quoc Nguyen (St. Vincent’s Hospital, Sydney); Pamela Palasanthrian (Sydney Children’s Hospital); Robert Pickles (infectious diseases physician, Taree), Robert Pritchard (Royal North Shore Hospital); Tania Sorrell (Westmead Hospital); Lex Tierney (John Hunter Hospital); Voula Tomasotos (Liverpool Hospital); Robert Vaz (Orange Base Hospital); Kerry Weeks (Royal North Shore Hospital). Queensland: Anthony Allworth (Royal Brisbane Hospital); Christopher Coulter (The Prince Charles Hospital); Joan Faoagali (Royal Brisbane Hospital); Barbara Johnson (Princess Alexandra Hospital), David Looke (Princess Alexandra Hospital), Joseph McCormack (The Mater Adult Hospital); Graeme Nimmo (Princess Alexandra Hospital); Gabrielle O’Kane (The Prince Charles Hospital); E. Geoffrey Playford (Princess Alexandra Hospital); Jennifer Robson (Sullivan and Nicolaides Pathology). South Australia: David Ellis (Women’s and Children’s Hospital); Rosemary Handke (Women’s and Children’s Hospital); Karen Rowlands (Royal Adelaide Hospital); David Shaw(Royal Adelaide Hospital). Tasmania: Louise Cooley (Royal Hobart Hospital); Erica Cox (Launceston General Hospital); Alistair McGregor (Royal Hobart Hospital). Victoria: Clare Franklin (Alfred Hospital); Cathy Joseph (St Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne), Tony Korman (Monash Medical Centre), Orla Morrissey (Alfred Hospital), Monica Slavin (Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre), Denis Spelman (Alfred Hospital); Bryan Speed (Austin and Repatriation Hospitals); Harsha Sheorey (St. Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne). Western Australia: Peter Boan (Royal Perth Hospital); John Dyer (Fremantle Hospital); Christopher Heath (Royal Perth Hospital); Dianne Gardam (Royal Perth Hospital); Duncan McLennan (Fremantle Hospital); Ronan Murray (Royal Perth Hospital); Todd Pryce (Royal Perth Hospital).