Volume 14, Number 3—March 2008
Research
Discovering and Differentiating New and Emerging Clonal Populations of Chlamydia trachomatis with a Novel Shotgun Cell Culture Harvest Assay
Figure 3
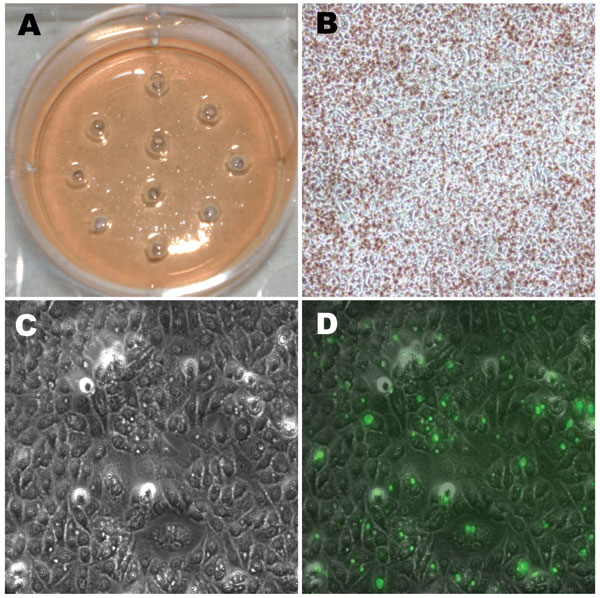
Figure 3. Photographs of light and fluorescent microscopy showing the shotgun cell culture harvest method for isolating clonal populations of clinically persistant strains. A) 1 well in a 6-well plate after harvesting 10 random areas using sterile pipettes; no plaques could be visualized in any well unlike the situation for the reference strains in Figure 2. B) The same well before harvesting infected areas (magnification ×100). C) Light microscopy view of an area with infected cells containing small inclusion bodies after agarose overlays had been removed (magnification ×400). D) Fluorescent microscopy view of the same field as in C (magnification ×400); infected cells were stained with Chlamydia trachomatis–specific lipopolysaccharide antibodies. Arrows denote small fluorescing inclusion bodies within the cell cytoplasm.