Volume 15, Number 1—January 2009
Dispatch
Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 Diversity, France
Figure 1
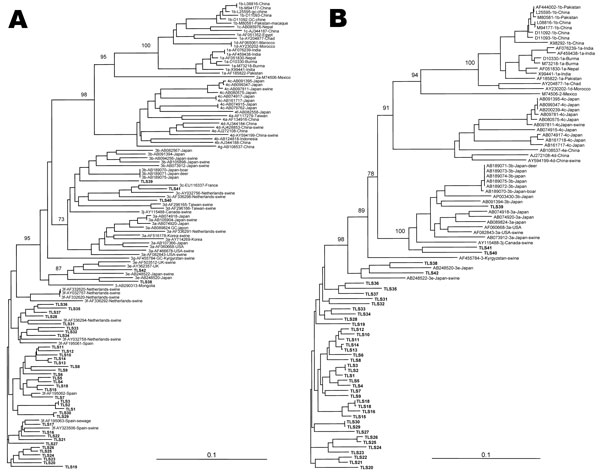
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationship among hepatitis E virus (HEV) strains from southwestern France and reference strains available in GenBank based on a 348-nt sequence in the open reading frame 2 (A) and on a 383-nt sequence of HEV RNA–dependent RNA polymerase (B). Genetic distances were calculated by using the Kimura 2-parameter method; phylogenetic trees were plotted by the neighbor-joining method. The reproducibility of the branching pattern was tested by bootstrap analysis (1,000 replicates). Each branch was labeled with the GenBank accession number of the strain, the geographic area, and the host, if nonhuman, and the geographic area where the sequence was isolated. The genotype and subtype were identified according to Lu et al. (3). Scale bars represent nucleotide substitutions per site. Boldface indicates the G3 French strains.
References
- Okamoto H. Genetic variability and evolution of hepatitis E virus. Virus Res. 2007;127:216–28. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lu L, Li C, Hagedorn CH. Phylogenetic analysis of global hepatitis E virus sequences: genetic diversity, subtypes and zoonosis. Rev Med Virol. 2006;16:5–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kamar N, Selves J, Mansuy JM, Ouezzani L, Peron JM, Guitard J, Hepatitis E virus and chronic hepatitis in organ-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:811–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mansuy JM, Peron JM, Abravanel F, Poirson H, Dubois M, Miedouge M, Hepatitis E in the south west of France in individuals who have never visited an endemic area. J Med Virol. 2004;74:419–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kabrane-Lazizi Y, Zhang M, Purcell RH, Miller KD, Davey RT, Emerson SU. Acute hepatitis caused by a novel strain of hepatitis E virus most closely related to United States strains. J Gen Virol. 2001;82:1687–93.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhai L, Dai X, Meng J. Hepatitis E virus genotyping based on full-length genome and partial genomic regions. Virus Res. 2006;120:57–69. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Inoue J, Takahashi M, Yazaki Y, Tsuda F, Okamoto H. Development and validation of an improved RT-PCR assay with nested universal primers for detection of hepatitis E virus strains with significant sequence divergence. J Virol Methods. 2006;137:325–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Inoue J, Takahashi M, Ito K, Shimosegawa T, Okamoto H. Analysis of human and swine hepatitis E virus (HEV) isolates of genotype 3 in Japan that are only 81–83% similar to reported HEV isolates of the same genotype over the entire genome. J Gen Virol. 2006;87:2363–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meng XJ, Purcell RH, Halbur PG, Lehman JR, Webb DM, Tsareva TS, A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:9860–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Banks M, Bendall R, Grierson S, Heath G, Mitchell J, Dalton H. Human and porcine hepatitis E virus strains, United Kingdom. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:953–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colson P, Kaba M, Bernit E, Motte A, Tamalet C. Hepatitis E associated with surgical training on pigs. Lancet. 2007;370:935. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drobeniuc J, Favorov MO, Shapiro CN, Bell BP, Mast EE, Dadu A, Hepatitis E virus antibody prevalence among persons who work with swine. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:1594–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li TC, Chijiwa K, Sera N, Ishibashi T, Etoh Y, Shinohara Y, Hepatitis E virus transmission from wild boar meat. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1958–60.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tei S, Kitajima N, Takahashi K, Mishiro S. Zoonotic transmission of hepatitis E virus from deer to human beings. Lancet. 2003;362:371–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar