Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Dispatch
Genomic Characterization of Novel Human Parechovirus Type
Figure 1
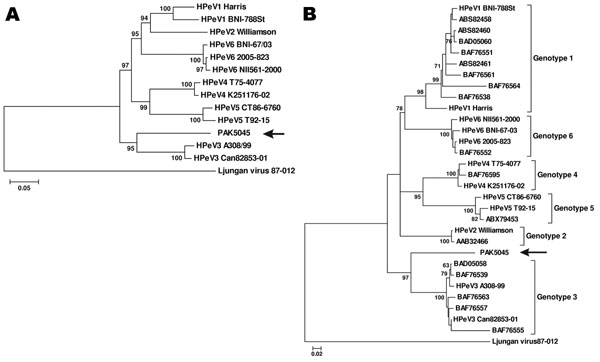
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of PAK5045 virus (arrows) and parechovirus strains based on A) the complete amino acid sequence of P1 region and B) the complete amino acid sequence of viral protein 1 (VP1). All parechovirus sequences were obtained from GenBank, including 13 completely sequenced parechoviruses, human parechoviruses (HPeV) 1 Harris (Q66578), HPeV1 BNI-788St (ABK54353), HPeV2 Williamson(CAA06679), HPeV3 A308/99(BAC23086), HPeV3 Can82853-01(CAI64373),HPeV4 K251176-02 (ABC41566), HPeV4 T75-4077 (CAJ84484), HPeV5 CT86-6760 (Q9YID8), HPeV5 T92-15 (CAJ84483),HPeV6 NII561-2000 (BAF63403), HPeV6 2005-823 (ABX79460), HPeV6 BNI-67/03 (ABS82455), Ljungan virus 87-012 (AAM46079), and 17 sequences with accession numbers shown directly on the tree. Both trees were constructed by the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates using MEGA4.