Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Dispatch
Tahyna Virus and Human Infection, China
Figure 2
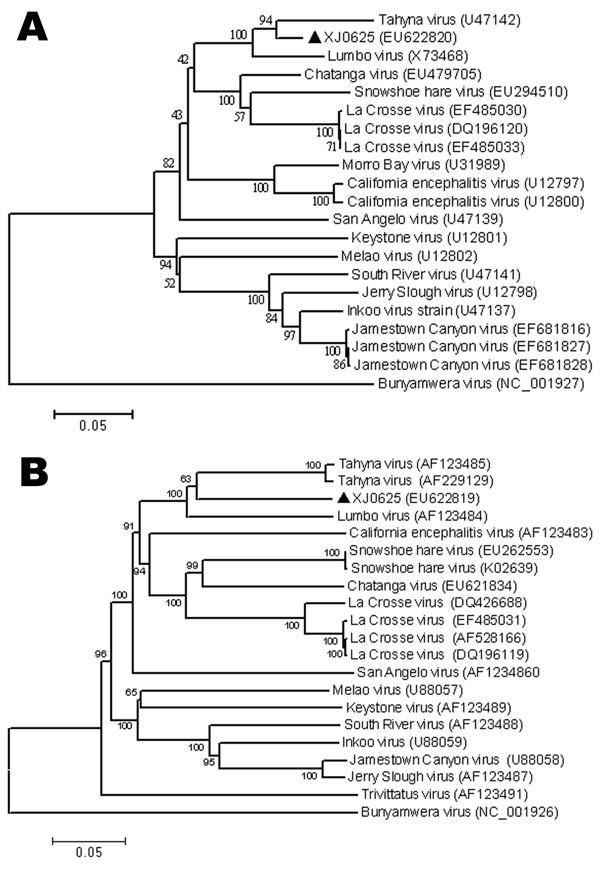
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of Tahyna virus (TAHV) XJ0625 from China based on the complete nucleotide sequence of the small segment (A) and the medium segment (B). Distances and groupings were determined by the p-distance algorithm and neighbor-joining method with MEGA version 3.1 software (www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values are indicated and correspond to 1,000 replications. The tree was rooted by using Bunyamwera virus as the outgroup virus. Scale bars indicate a genetic distance of 0.05-nt substitutions per position.
Page created: December 08, 2010
Page updated: December 08, 2010
Page reviewed: December 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.