Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Research
Bacterial Phenotype Variants in Group B Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome1
Figure 7
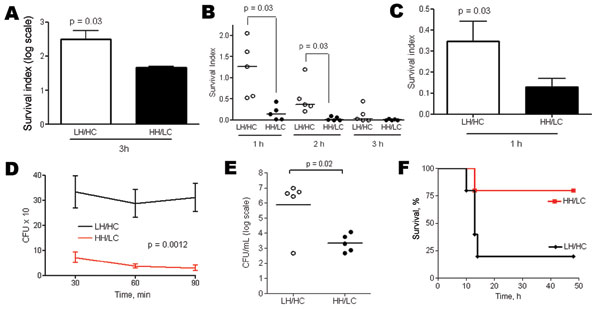
Figure 7. A) Human whole-blood killing assay after 3 h incubation, using 100 CFU bacteria in 100 μL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and 300 μL blood. Error bars indicate SEM. B) 100 CFU bacteria in 100 μL PBS and 1,000 μL blood. Survival index is calculated as follows: (CFU at the end of the assay)/(CFU at t = 0 h). Horizontal lines indicate the median. C) Opsonophagocytic killing assay after 1 h incubation, using a multiplicity of infection of ≈1:1 (CFU 106/mL: neutrophils 106/mL) and 10% volume serum. Error bars indicate SEM. D) Intracellular survival assays in neutrophils after 30, 60, and 90 min of extracellular antimicrobial drug exposure. Error bars indicate SEM. E) Murine model for invasive disease (low inoculum). Groups of 5 mice were inoculated intraperitoneally with 6–8 × 106 CFU of low hemolytic (LH)/high encapsulation (HC) or high hemolytic (HH)/low encapsulation (LC) group B streptococcal isolates per mouse. Levels of bacteremia were assessed after 6 h. Horizontal lines indicate the median. F) Kaplan-Meier survival plot.
1Part of this work was presented at Lancefield 2008 International Symposium on Streptococci and Streptococcal Diseases, Porto Heli, Greece, June 22–26, 2008.
2Current affiliation: Clinic for Infectious Diseases, University Hospital Bern, Bern, Switzerland.