Volume 15, Number 3—March 2009
Research
Prevalence and Seasonality of Influenza-like Illness in Children, Nicaragua, 2005–2007
Figure 2
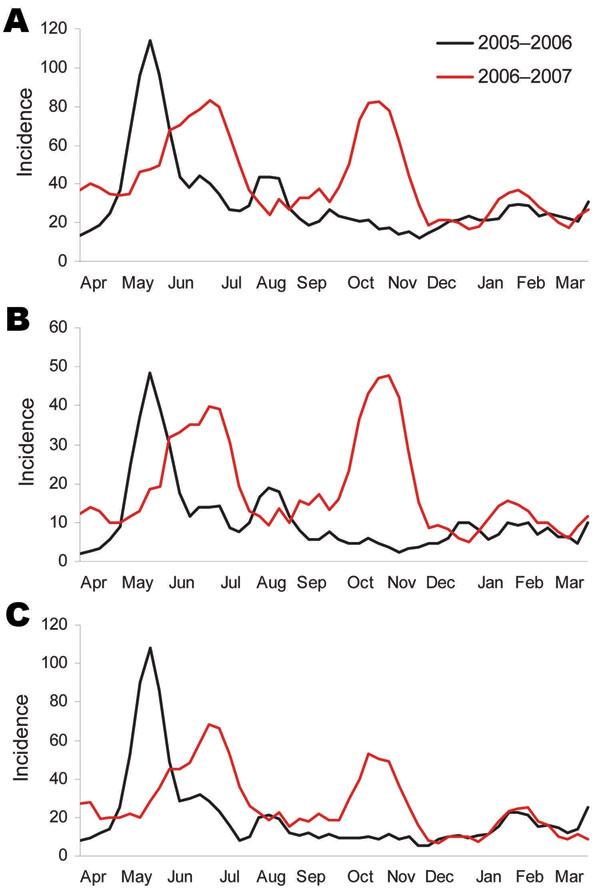
Figure 2. Incidence (cases/100 person-years) of influenza-like illness (ILI) in a cohort of children in Nicaragua, showing seasonal peaks, April 16, 2005–April 15, 2006, and April 16, 2006–April 15, 2007. A) Incidence of ILI episodes per calendar week. B) Incidence of high-probability ILI episodes per calendar week. C) Incidence of ILI in children 6–12 years of age per calendar week. All curves were smoothed by Lowess (19) by using a 3-week moving average.
References
- Simonsen L. The global impact of influenza on morbidity and mortality. Vaccine. 1999;17(Suppl 1):S3–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Monto AS. Global burden of influenza: what we know and what we need to know. Int Congr Ser. 2004;1263:3–11. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Viboud C, Alonso WJ, Simonsen L. Influenza in tropical regions. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e89. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Influenza: report by the Secretariat. Fifty-sixth World Health Assembly. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003.
- Straliotto SM, Siqueira MM, Muller RL, Fischer GB, Cunha ML, Nestor SM. Viral etiology of acute respiratory infections among children in Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2002;35:283–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tsai HP, Kuo PH, Liu CC, Wang JR. Respiratory viral infections among pediatric inpatients and outpatients in Taiwan from 1997 to 1999. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:111–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sung RY, Chan RC, Tam JS, Cheng AF, Murray HG. Epidemiology and aetiology of acute bronchiolitis in Hong Kong infants. Epidemiol Infect. 1992;108:147–54.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Arruda E, Hayden FG, McAuliffe JF, de Sousa MA, Mota SB, McAuliffe MI, Acute respiratory viral infections in ambulatory children of urban northeast Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1991;164:252–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dosseh A, Ndiaye K, Spiegel A, Sagna M, Mathiot C. Epidemiological and virological influenza survey in Dakar, Senegal: 1996–1998. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:639–43.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rao BL, Banerjee K. Influenza surveillance in Pune, India, 1978–90. Bull World Health Organ. 1993;71:177–81.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chew FT, Doraisingham S, Ling AE, Kumarasinghe G, Lee BW. Seasonal trends of viral respiratory tract infections in the tropics. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;121:121–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wong CM, Yang L, Chan KP, Leung GM, Chan KH, Guan Y, Influenza-associated hospitalization in a subtropical city. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e121. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nguyen HL, Saito R, Ngiem HK, Nishikawa M, Shobugawa Y, Nguyen DC, Epidemiology of influenza in Hanoi, Vietnam, from 2001 to 2003. J Infect. 2007;55:58–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Monto AS. Epidemiology of viral respiratory infections. Am J Med. 2002;112(Suppl 6A):4S–12S. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zambon MC, Stockton JD, Clewley JP, Fleming DM. Contribution of influenza and respiratory syncytial virus to community cases of influenza-like illness: an observational study. Lancet. 2001;358:1410–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fleming DM, Pannell RS, Elliot AJ, Cross KW. Respiratory illness associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus infection. Arch Dis Child. 2005;90:741–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Call SA, Vollenweider MA, Hornung CA, Simel DL, McKinney WP. Does this patient have influenza? JAMA. 2005;293:987–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ohmit SE, Monto AS. Symptomatic predictors of influenza virus positivity in children during the influenza season. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:564–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chambers JM, Cleveland WS, Tukey PA. Graphic methods for data analysis (The Wadsworth statistics/probability series). Pacific Grove (CA): Duxbury Press; 1983.
- Monto AS, Napier JA, Metzner HL. The Tecumseh study of respiratory illness. I. Plan of study and observations on syndromes of acute respiratory disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1971;94:269–79.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Neuzil KM, Wright PF, Mitchel EF Jr, Griffin MRBBBBBBJ. Pediatr. 2000;137:856–64.The burden of influenza illness in children with asthma and other chronic medical conditions. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Koch A, Molbak K, Homoe P, Sorensen P, Hjuler T, Olesen ME, Risk factors for acute respiratory tract infections in young Greenlandic children. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;158:374–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Selwyn B. The epidemiology of acute respiratory tract infections in young children: comparison of findings from several developing countries. Coordinated Data Group of BOSTID Researchers. Rev Infect Dis. 1990;12(Suppl 8):870–88.
Page created: December 07, 2010
Page updated: December 07, 2010
Page reviewed: December 07, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.