Volume 15, Number 9—September 2009
Research
Clinical Assessment and Improved Diagnosis of Bocavirus-induced Wheezing in Children, Finland
Figure 2
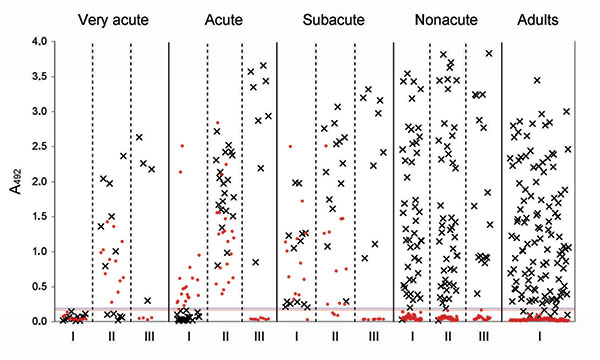
Figure 2. Scatter plots of individual absorbance values at 492 nm (A492) of immunoglobulin (Ig) G (×) and IgM (red dots) against human bocavirus (HBoV) in enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) for acute-phase (I), convalescence-phase (II), and 5-year follow-up (III) serum samples from wheezing children and single serum samples from young healthy adults, Finland. The 45 children with confirmed acute HBoV infections (by viremia and serodiagnosis) were divided into 3 groups according to the degree of acuteness (very acute, acute, and subacute) on the basis of findings in I and II serum samples. Very acute, I sample seronegative but II sample IgM positive (n = 12); acute, I sample IgM positive but IgG showed seroconversion (n = 20); subacute, IgG positive with a diagnostic increase or constant level in I and II samples, IgM positive (n = 13). Also shown are results for children without viremia or serodiagnosis (nonacute [for only the first 45 children with seropositive samples]), and young healthy adults (n = 115). EIA cutoffs are indicated by a blue line (IgG; 0.188) or a red line (IgM; 0.167). Dots below the cutoff lines indicate samples with absorbance values less than the negative cutoff values (i.e., IgM– and IgG– results).