Volume 15, Number 9—September 2009
Research
Predicting Phenotype and Emerging Strains among Chlamydia trachomatis Infections
Figure 2
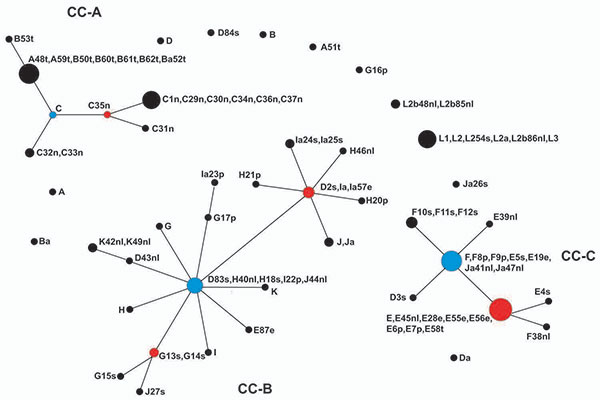
Figure 2. eBURST population snapshot for Chlamydia trachomatis isolates. Sequence types (STs) that are linked differ at single multilocus sequence typing locus and represent clonal complexes. Strains in the same clonal complexes are likely descended from the same recent ancestor. Each circle represents a ST. An ST in blue is most likely the primary founder of the clonal complex; STs in red are subgroup founders. The number of isolates of each ST is represented by the area of the circle. Clonal complex A (CC-A) for trachoma strains; CC-B, noninvasive, nonprevalent urogenital strains; and CC-C, noninvasive, globally prevalent urogenital strains. The eBURST report is shown in the Technical Appendix.
Page created: December 07, 2010
Page updated: December 07, 2010
Page reviewed: December 07, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.